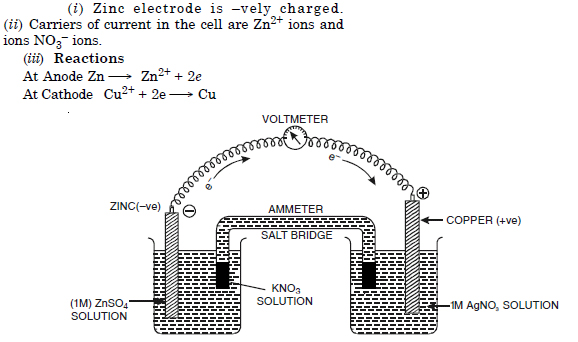
Question 1:
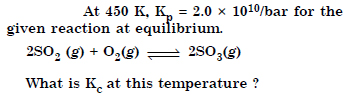
Answer:
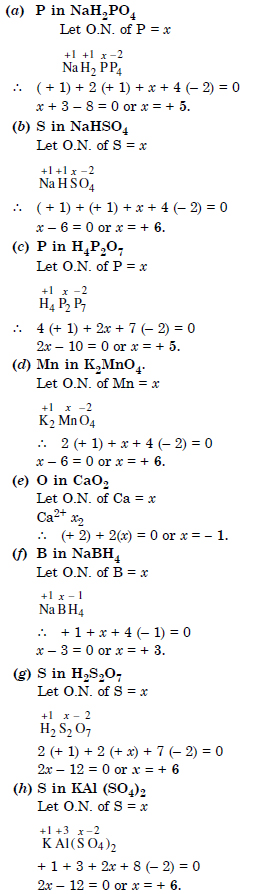
Question 2:
What are the oxidation numbers of the underlined elements in each of the following and how do you rationalise your results ?
Answer:
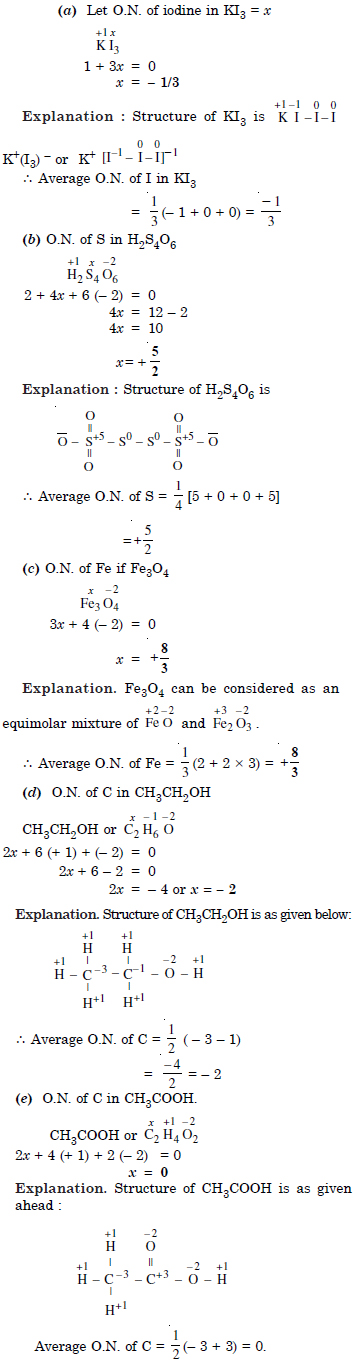
Question 3:
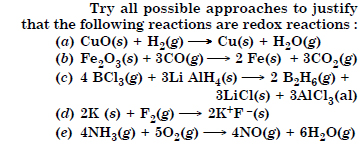
Answer:
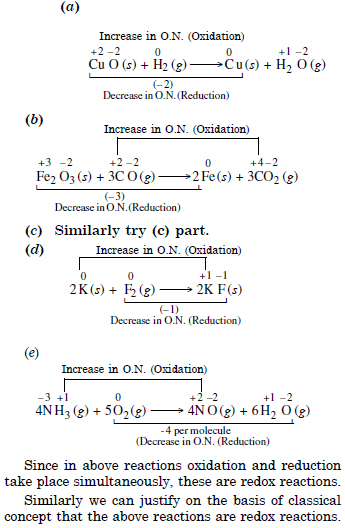
Question 4:
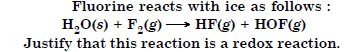
Answer:
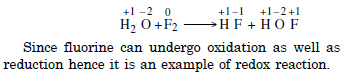
Question 5:
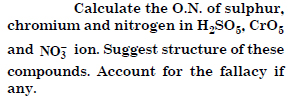
Answer:
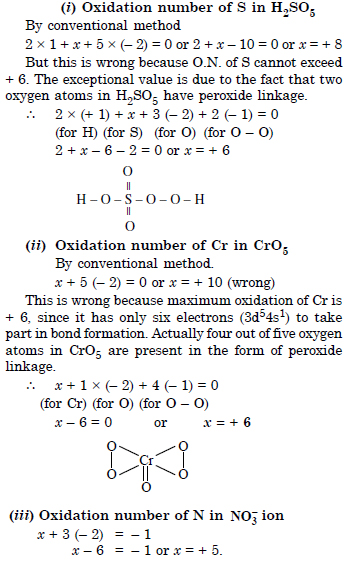
Question 6:
Write the formulae of following compound :
(a) Mercury (II) chloride
(b) Nickel (II) sulphate
(c) Tin (IV) oxide
(d) Thallium (I) sulphate
(e) Ion (III) sulphate
(f) Chromium (III) oxide.
Answer:
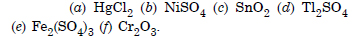
Question 7:
Suggest a list of substances where carbon can exhibit oxidation states from – 4 to + 4 and nitrogen from – 3 to + 5.
Answer:
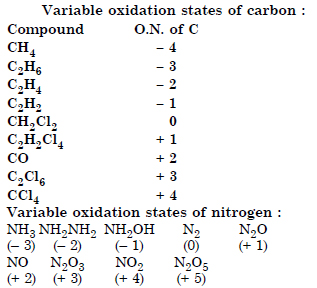
Question 8:
While sulphur dioxide and hydrogen peroxide can act as oxidising as well as reducing agents in their reactions, ozone and nitric acid can act only as oxidising agents. Why ?
Answer:

Question 9:
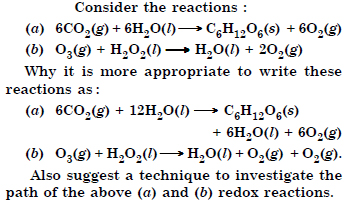
Answer:
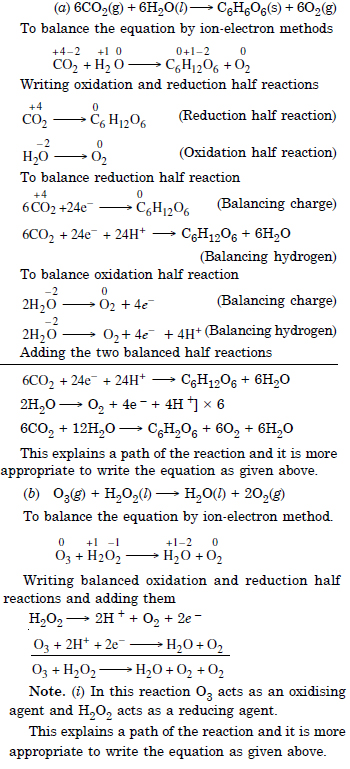
Question 10:
The compound AgF2 is unstable compound. However if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidising agent. Why ?
Answer:

Question 11:
Whenever a reaction between an oxidising agent and a reducing agent is carried out, a compound of lower oxidation state is formed if the reducing agent is in excess and a compound of higher oxidation state is formed if the oxidising agent is in excess. Justify this statement giving three illustrations.
Answer:
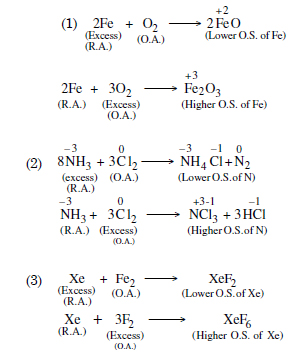
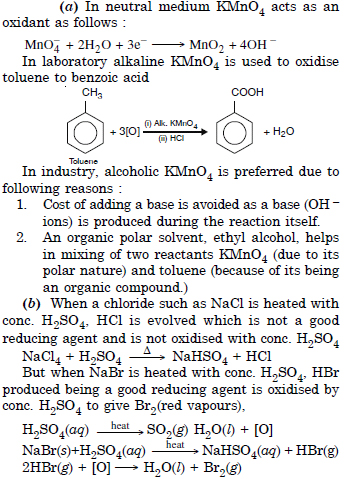
Question 12:
How do you account for the following observations ?
(a) Though alkaline postassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of
benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why ? Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction.
(b) When concentrated sulphuric acid is added to an inorganic mixture containing chloride, we get a colourless pungent smelling
gas HCl. However, if mixture contains bromide, then red vapours of bromine are evolved. Why ?
Answer:
Question 13:
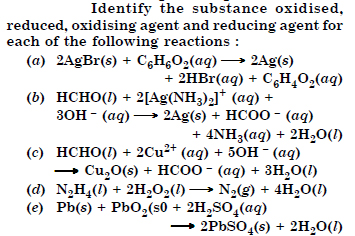
Answer:
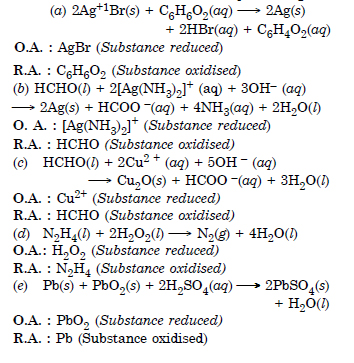
Question 14:
Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine ?
Answer:
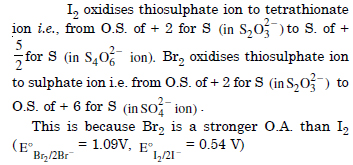
Question 15:
Justify giving reactions that among halogens, fluorine is the best oxidant and among hydrohalic compounds, hydroiodic acid is the best reductant.
Answer:

Question 16:
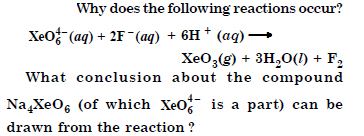
Answer:
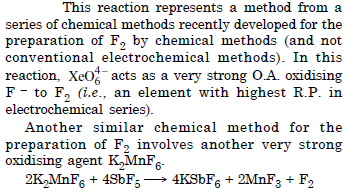
Question 17:
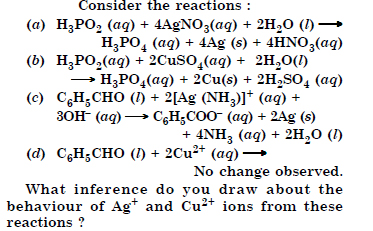
Answer:

Question 18:
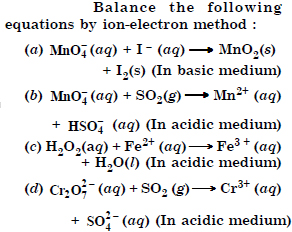
Answer:
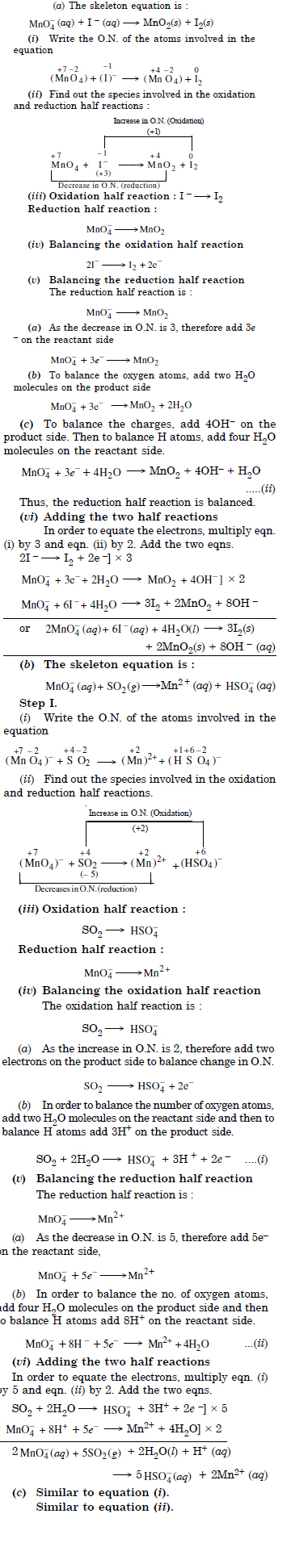
Question 19:

Answer:
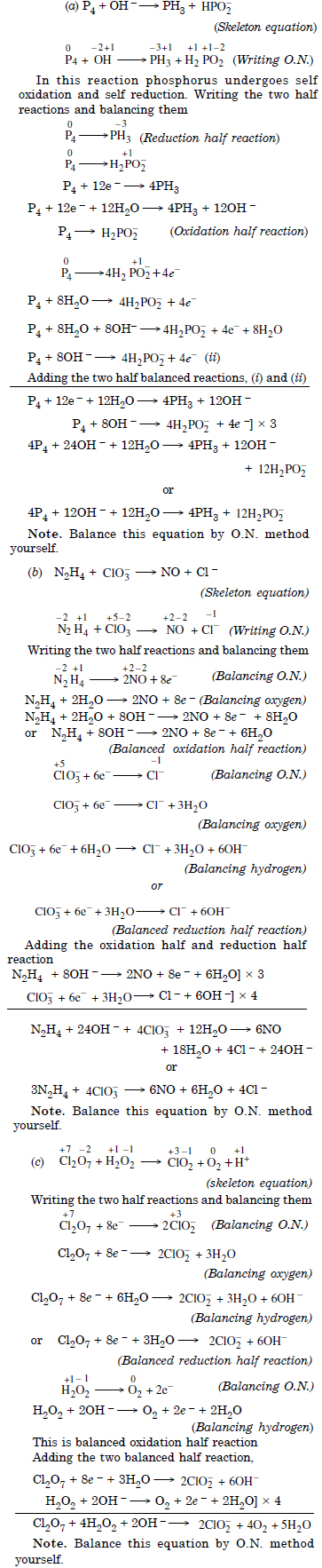
Question 20:
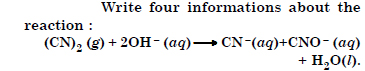
Answer:
(i) It involves the decomposition of cyanogen (CN)2 in the alkaline medium.
(ii) Cyanogen undergoes disproportionation in the reaction.
(iii) It is an example of redox reaction.
(iv) (CN)2 is a pseudohalogen and CN – is a pseudohalide ion.
Question 21:
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2 and H+ ion. Write balanced ionic equation of the reaction.
Answer:
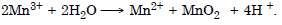
Question 22:
Consider the elements : Cs, Ne, I, F
(i) Identify the element that exhibits only – ve oxidation state.
(ii) Identify the element that exhibits only + ve oxidation state.
(iii) Identify the element that exhibits + ve and – ve oxidation states.
(iv) Identify the element that neither exhibits + ve and – ve oxidation states.
Answer:
(i) F (fluorine),
(ii) Cs (cesium),
(iii) I (iodine),
(iv) Ne (neon).
Question 23:
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Answer:
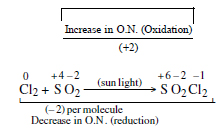
Question 24:
Refer to the periodic table given in your book and select three non-metals and three metals which can show disproportionation reactions.
Answer:
Non-metals which can exist in variable oxidation states can show disproportionation reactions. For example, phosphorus, chlorine, sulphur. Metals belonging to d-block elements can show disproportionation reactions. For example, manganese, iron, copper.
Question 25:
In the Ostwald process for the manufacture of nitric and, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.0 g of ammonia and reacting with 20.0 g of oxygen ?
Answer:
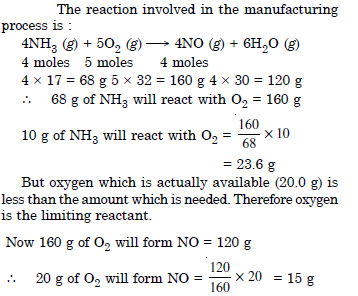
Question 26:

Answer:
(a) Feasible
(b) Feasible
(c) Feasible
(d) Not feasible
(e) Not feasible.
Question 27:
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following :
(1) An aqueous solution of AgNO3 with silver electrodes.
(2) A aqueous solution AgNO3 with Platinum electrodes.
(3) A dilute solution of H2SO4 with Platinum electrodes.
(4) An aqueous solution of CuCl2 with Platinum electrodes.
Answer:
(i) At cathode : Ag is deposited At anode : Ag + ions pass into solution.
(ii) At cathode : Ag is deproduced. At anode : O2 is produced.
(iii) At cathode : H2 is produced. At anode : O2 is produced.
(iv) At cathode : Copper is deposited. An anode : O2 is produced.
Question 28:
Arrange the following metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts. Al, Cu, Fe, Mg & Zn.
Answer:
Decreasing order of displacement Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu.
Question 29:
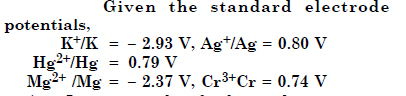
Answer:
Increasing order of reducing character is Ag < Hg < Cr < Mg < K.
Question 30:
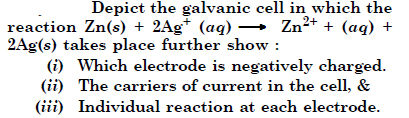
Answer: