Board Paper of Class 10 2022 Science (Theory) Term 1 Set 031/2/4 - Solutions
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 60 questions out of which 50 questions are to be attempted.All questions carry equal marks.
- Question paper consists of three sections - Section A,B, and C.
- Section - A consists 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Q.No. 1 to 24.
- Section - B also consists 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Q.No. 25 to 48.
- Section - C consists of three case Studies containing 12 questions and 4 questions in each case. Attempt any 10 from Q.No. 49 to 60.
- There is only correct option for Multiple Choise Question (MCQ). Marks will not be awarded for answering more than one option.
- There is no negative marking.
Question 1
A Student Sodium Sulphate solution in a test tube and added Barium Chloried solution to it. He obsorved that an insoluble substance has formed. The colour and moleculer formula of the insoluble substance is:
- Grey, Ba2SO4
- Yellow, Ba(SO4)2
- White, BaSO4
- Pink, BaSO4
Answer: (C)
Explanation :
It’s a reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride and the product is barium sulphate which is whitish in colour and remain insoluble.
Question 2
Which of the following oxide(s) is/are Soluble in water to form alkalie ?
- Na2O
- SO2
- K2O
- NO2
- (i) and (iii)
- (i) only
- (ii) and (iv)
- (iii) only
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
(Alkaline sodium Hydroxide )
(Alkaline Potassium Hydroxide)
Question 3
Study the diagram given below and identify the gas formed in the reaction.
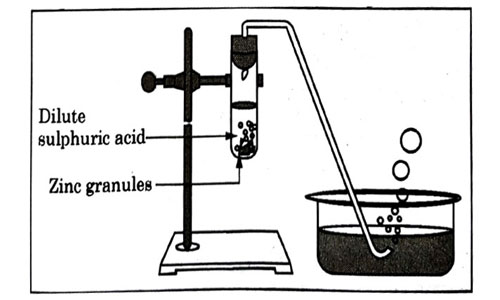
- Carbon dioxide which extinguishes the burning candle.
- Oxygen due to which the candle burns more brightly.
- Sulphur dioxide which produces a suffocating smell.
- Hydrogen which while burning produces a popping sound.
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Hydrogen gas produces popping sound.
Question 4
Sodium reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The balanced equation which represents the above reaction is;
Answer: (b)
Question 5
Which of the options in the given table are correct?
| Option | Natural Source | Acid Present |
|---|---|---|
| (i) | Orange | Oxalic acid |
| (ii) | Sour milk | Lactic acid |
| (iii) | Ant sting | Methanoic acid |
| (iv) | Tamarind | Acetic acid |
- (i) and (ii)
- (i) and (iv)
- (ii) and (iii)
- (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (c)
Explanation : Orange contains citric acid and tamarind contains tartaric acid.
Question 6
The above reaction is a/an
- displacement reaction
- endothermic reaction
- exothermic reaction
- neutralisation reaction
Answer: (c)
Explanation : It’s the oxidation of food to produce energy means exothermic reaction (heat/energy liberated in the reaction).
Question 7
Which of the following statements about the reaction given below are correct?
- is oxidized to
- is reduced to
- acts as an oxidizing agent
- acts as an oxidizing agent
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i) and (ii) only
- (iii) and (iv) only
Answer: (c)
Explanation :
(Oxidation number of Cl increases.)
(Oxidation number of Mn decreases.)
Question 8
Select from the following the statement which is true for bases.
- Bases are bitter and turn blue litmus red.
- Bases have a pH less than 7
- Bases are sour and change from red litmus to blue.
- Bases turn pink when a drop of phenolphthalein is added to them.
Ans: (d)
Explanation : Bases are bitter and turn red litmus blue. Bases have a pH more than 7
Question 9
Study the following table and choose the correct option:
| SL No. | Salt | Parent Acid | Parent Base | Nature of Salt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | Solidum Chloride | NaOH | Basic | |
| (b) | Sodium Carbonate | NaOH | Neutral | |
| (c) | Sodium Sulphate | NaOH | Acidic | |
| (d) | Sodium Acetate | NaOH | Basic |
Answer: (d)
Explanation - Sodium hydroxide is a strong base and salt formed will be basic.
Question 10
It is important to balance the chemical equations to satisfy the law of conservation of mass. Which of the following statements of the law is incorrect?
- The total mass of the elements present in the reactants is equal to the total mass of the elements present in the products.
- The number of atoms of each element remains the same, before and after a chemical reaction.
- The chemical composition of the reactants is the same before and after the reaction
- Mass can neither be created nor can it be destroyed in a chemicalReaction.
Answer: (c)
Explanation - During a chemical reaction chemical composition changes.
Question 11
Consider the following statements in connection with the functions of the blood vessels marked A and B in the diagram of a human heart as shown.
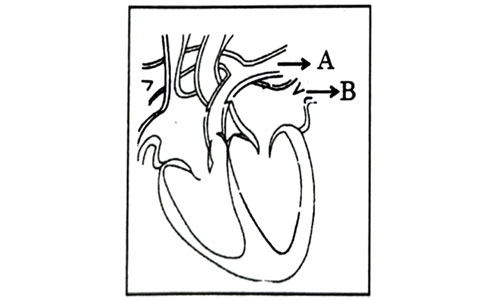
- Blood vessel A – It carries carbon dioxide rich blood to the lungs.
- Blood vessel B – It carries oxygen rich blood from the lunga.
- Blood vessel B – Left atrium relaxes as it receives blood from this blood vessel
- Blood vessel A – Right atrium has thick muscular wall as it has to pump blood to this blood vessel.
- (i) and (ii) only
- (ii) and (iii) only
- (ii),(iii) and (iv)
- (i),(ii) and (iii)
Answer: (d)
Explanation : Blood vessel A represents pulmonary artery which is the only artery carrying deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Blood vessel B represents pulmonary veins which is the only vein carrying oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium. The left atrium relaxes when it is collecting this blood and contracts to pump this blood to left ventricle.
Question 12
In Living organisms During respiration which of the following Products are not formed if oxygen is not available?
- Carbon dioxide + Water
- Carbon dioxide + Alcohol
- Lactic acid + Alcohol
- Carbon dioxide + Lactic Acid
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
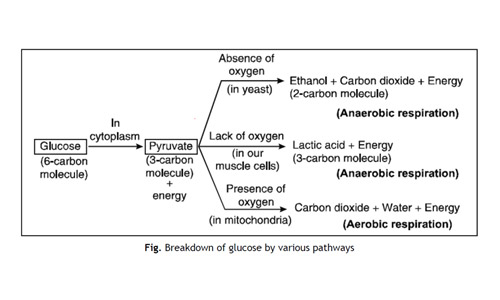
Question 13
The Correct Statements with reference to single called organisms are
- Complex substances are not broken down in to simpler substances.
- Simple diffusion is sufficient to meet the requirement of exchange of gases.
- Specialized tissues perform different functions in the organism.
- Entire surface of the organism is in contact with the environment for taking in food.
- (i) and (iii)
- (ii) and (iii)
- (ii) and (iv)
- (i) and (iv)
Answer: (c)
Explanation : In unicellular organisms, diffusion across the cell membrane is sufficient for supplying oxygen to the whole body. Diffusion is a slow and passive process. Unicellular organisms can absorb sufficient oxygen because of its complete body contact with the surrounding environment.
Question 14
Which one among the following is not removed as a waste product from the body of a plant?
- Resins and Gums
- Urea
- Dry Leaves
- Excess Water
Answer: (b)
Explanation : Any substance that oozes out from the pores of diseased or injured plant tissue is called as exudate. The process of oozing out of substances from plant is termed as exudation. Resins, gums, oils and water are examples of exudates widely extracted for industrial uses.
Question 15
Which one of the following statements are correct in reference to the role of A (Shown in the given diagram) during a breathing cycle in human beings?
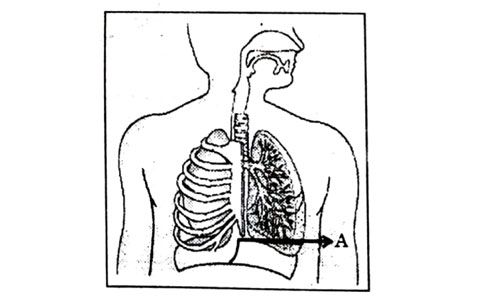
- It helps to decrease the residual volume of air in lungs.
- It flattens as we inhale.
- It gets raised as we inhale.
- It helps the chest cavity to become larger.
- (ii) and (iv)
- (iii) and (iv)
- (i) and (ii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
Answer: (d)
Explanation : Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the thoracic cavity or chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs. Upon exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its domelike shape, and air is forced out of the lungs.
Question 16
Which one of the following conditions is true for the state of stomata of a green leaf shown in the given diagram?
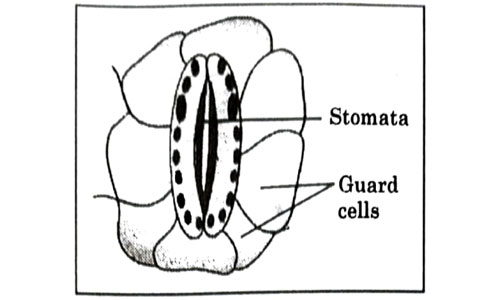
- Large amount of water flows in to the ground cells.
- Gaseous exchange is occurring in large amount.
- Large amount of water flows out from the guard cells.
- Large amount of sugar collects in the guard cell
Answer: (c)
Explanation : The stomata are surrounded by two guard cells which regulate its opening and closing. Stomata are open during the day time for gaseous exchange and also release water vapour through transpiration. The opening and closing of stomata is due to the change in turgor pressure of the guard cell.
Question 17
In which of the following is a concave mirror used?
- A solar cooker
- A rear view mirror in vehicles
- A safety mirror in shopping malls
- In Viewing full size image of distant tall buildings.
Answer: (a)
Explanation : In solar cooker, beam of sunlight falls on concave reflector which then focus/converge it on small cooking area at focal point.
Question 18
A student wants to obtain magnified image of an object AB as on a Screen. Which one of the following arrangements shows the correct position of AB for him/her to be successful?
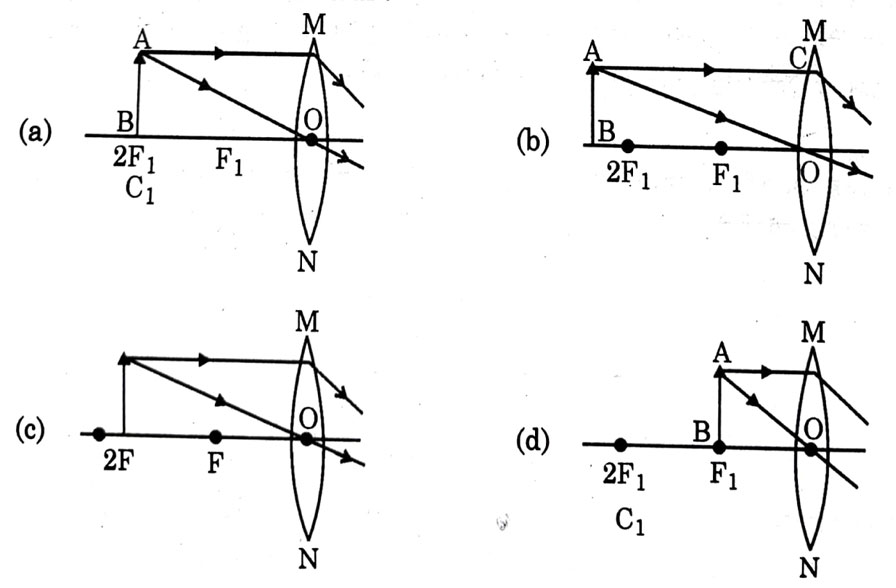
Answer: (c)
Explanation - To get real & magnified image, object should be kept either between 2F and F or at F. If it is kept at F, image will form at infinity which cannot be taken on screen, so object should be kept between 2F and F.
Question 19
The following diagram shows the use or an optical device to perform an experiment of light. As per the arrangement shown, the optical device is likely to be a;
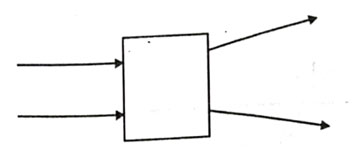
- Concave mirror
- Concave lens
- Convex mirror
- Convex lens
Answer: (b)
Explanation - Here ray is passing though this device so it should be a lens. Also rays are diverging, so it should be a concave lens.
Question 20
A ray of light starting from air passes through medium A of refractive index 1.50, enters medium B of refractive index 1.33 and finally enters medium C of refractive index 2.42. If this ray emerges out in air from C, then for which of the following pairs of media the bending of light least?
- air-A
- A-B
- B-C
- C-air
Answer: (b)
Explanation : We have to take ratio of higher refractive index to lower refractive index when light travels from one media to other media. Lower ratio shows lower deviation or vise-versa. Lowest ratio value will be for media A-B, so bending of light will be least.
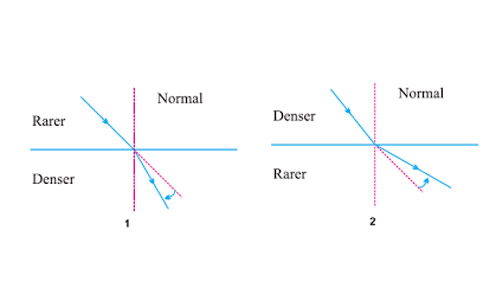
Let refractive index of rarer medium be
Let refractive index of denser medium be
When ray travels from rarer to denser medium,
If is high, is larger than . So, which means deviation is high.
When ray travels from denser to rarer medium,
If is low, is larger than . So, which means deviation is high.
So, Air - A, ratio =
A - B, ratio = (smallest)
B - C, ratio =
C - air, ratio = (largest)
Question 21
Which of the following statements is not true for scattering of light?
- Colour of the scattered tight depends on the size of particles of the atmosphere.
- Red light is least scattered in the atmosphere.
- Scattering of light takes place as various colours of white light travel with different speed in fir.
- The fine particles in the atmospheric air scatter the blue, light more strongly than red. So the scattered blue light enters our eyes.
Answer: (c)
Explanation - Scattering has no relation with speed of light as all constituent colours travel with same speed.
Question 22
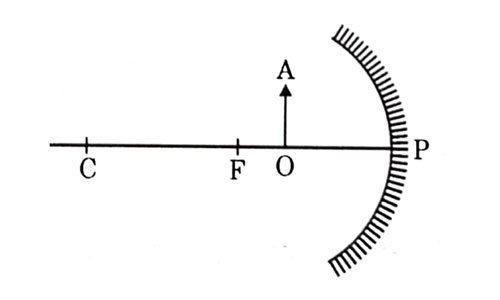
For the diagram shown according to the new Cartesian sign convention the magnification of the image formed will have the following specifications:
- Sign – Positive, Value — Leas than 1
- Sign — Positive, value – More than 1
- Sign — Negative, Value — Less than 1
- Sign Negative, value — More than 1ospheric air scatter the blue, light more strongly than red. So the scattered blue light enters our eyes.
Answer: (b) Sign — Positive, Value — More than 1
Explanation - When object is kept between F and P of concave mirror, image formed is virtual, erect and magnified. Location is behind the mirror, so magnification is more than 1 and positive.
Question 23
A ray of light is incident as shown. If A, B and C are three different transparent media. then which among the following options is true for the given Diagram?
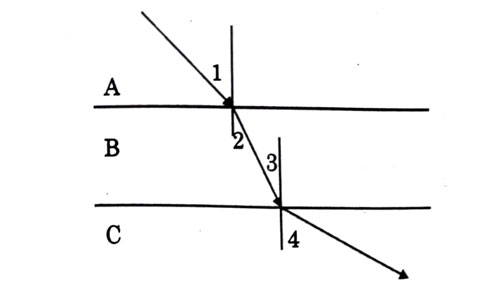
Answer: (c)
Explanation - As we can see from diagram, light bends towards normal while passing from A to B, therefore . Now, it travels through B on straight path. As interface between A - B and between B - C are parallel, so are alternate interior angles and equal (). Now from B to C, light moves away from normal, so . Also, if we extend ray in medium A, we will see that it will intersect actual ray in C which shows that .
Question 24
In the diagram given below X and Y are the end colours of the specturm of white light. The colour of ‘Y’ Represents the
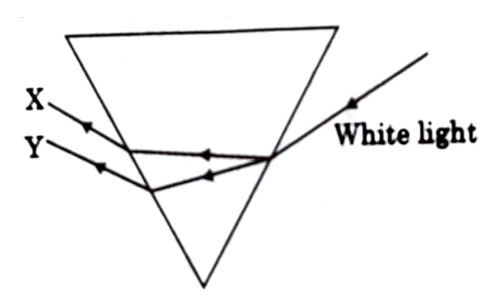
- Colour of sky as seen from earth during the day.
- Colour of the sky as seen from the moon.
- Colour used to paint the danger signals.
- Colour of sun at the time of noon
Answer: (c)
Explanation : As we know, in dispersion, red color deviates the least and violet color deviates the most, so Y is red which is also the colour used to paint the danger signals.
Question 25
Which one of the following reactions is categorised as thermal decomposition reaction ?
Answer: (d)
Explanation : Calcium carbonate on heating produces carbon dioxide gas and calcium oxide.
Question 26
Consider the pH value of the following acidic samples:
| S. No. | Sample | pH Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lemon Juice | 2.2 |
| 2 | Gastric Juice | 1.2 |
| 3 | Vinegar | 3.76 |
| 4 | Dil. Acetic acid | 3.0 |
The decreasing order of their H+ ion concentration is
- 3 > 4 > 1 > 2
- 2 > 1 > 3 > 4
- 2 > 1 > 4 > 3
- 3 > 4 > 2 > 1
Answer: (c)
Explanation – Lower pH value means higher H+ ions concentration.
Question 27
Consider the pH value of the following acidic samples:
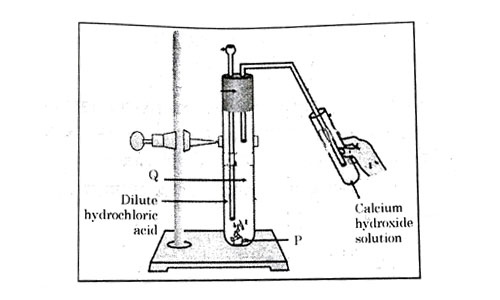
| Option | P | Q | Change observed in calcium hydroxide solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | gas | No Change | |
| (b) | gas | No Change | |
| (c) | gas | Turns milky | |
| (d) | gas | Turns milky |
Answer: (d)
Explanation :
Question 28
Which one of the following structures correctly depicts the compound CaCl2?
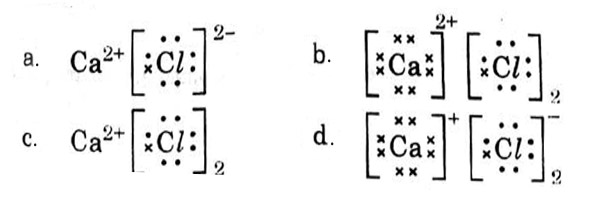
Answer: (c)
Explanation :
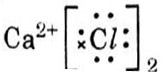
Question 29
The pair(s) which will show displacement reaction is/are
- solution and copper metal
- solution and copper metal
- solution and magnesium metal
- solution and iron metal
- (ii) only
- (ii) and (iii)
- (iii) and (iv)
- (i) and (ii)
Answer: (b)
Explanation : Copper is more reactive than silver and magnesium is more reactive than aluminium.
Question 30
Which of the following salts do not have the water of crystalisation ?
- Bleaching Powder
- Plaster of Paris
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- (ii) and (iv)
- (i) and (iii)
- (ii) and (iii)
- (i) and (iv)
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Bleaching powder – CaOCl2
Plaster of Paris – CaSO4.1/2H2O
Washing Soda – Na2CO3.10H2O
Baking Soda – NaHCO3
Question No. 31-35
Consists of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below :
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Question 31
Assertion (A) : Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as an ingredient in antacids.
Reason (R) : is a mild non-corrosive basic salt.
Answer: (a)
Explanation : Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a mild base which can be used as an antacid.
Question 32
Assertion (A) : Burning of Natural gas is an endothermic process
Reason (R) : Methane gas combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Answer: (c)
Explanation : Burning of natural gas is an exothermic process.
Question 33
Assertion (A) : Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and is taken up by plants in the form of inorganic nitrates or nitrites.
Reason (R) : The soil is the nearest and richest source of raw materials like Nitrogen, Phosphorus and other minerals for the plants.
Answer: (b)
Explanation : Nitrogen is a vital element as it is the major component of chlorophyll. It is a compound by which plants use sunlight to produce sugars from water and carbon dioxide by the process of photosynthesis. It is also a major component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Without proteins, plants wither and die.
Question 34
Assertion (A) : Sun appears reddish at the time of Sunrise and Sunset.
Reason (R) : Distance travelled by sunlight in the atmosphere is lesser during sunrise and sunset as compared to noon.
Answer: (c)
Explanation : Sun appears reddish during sunrise or sunset because sunlight travels greater distance/path in atmosphere as compared to noon. So, high scattering of blue light takes place and red light reaches us.
Question 35
Assertion (A) : Hydrochloric acid helps in the digestion of food in the stomach.
Reason (R) : Hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium to activate protein digesting enzymes.
Answer: (a)
Explanation : Walls of stomach releases hydrochloric acid which provide acidic medium for pepsin enzyme to act on proteins.
Question 36
A student was asked to write a stepwise procedure to demonstrate that carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis. He wrote the following steps. The wrongly worded step is –
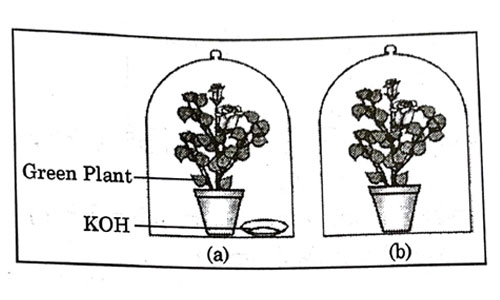
- Both potted plants are kept in dark room for at least three days.
- Bottom of the bell jars is sealed to make them air tight.
- Both potted plants are kept in sunlight after the starch test.
- A leaf from both the plants is taken to test the presence of starch.
Answer: (c)
Explanation : Plant needs three things for photosynthesis that is carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. In this experiment plants are kept airtight with the presence of potassium hydroxide which absorbs all the carbon dioxide present in the jar. Step 3 is not an essential step of experiment, but we can place plants in open after experiment.
Question 37
Respiratory structures of two different animals-a fish and a human being are as shown. Observe (a) and (b) and select one characteristic that holds true for both of them.
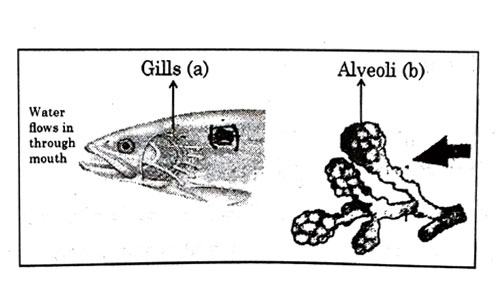
- Both are placed internally in the body of animal.
- Both have thin and moist surface for gaseous exchange.
- Both are poorly supplied with blood vessels to conserve energy.
- In both the blood returns to the heart after being oxygenated
Answer: (b)
Explanation : A respiratory organ consists of a surface across which gaseous exchange by simple diffusion can occur between blood and either water or air.The surface must be moist enough to allow the cells to permit sufficient gas exchange and thin enough to permit rapid diffusion.
Question 38
Observe the diagram of an activity given below. What does it help to conclude, when the person exhales into the test-tube ?
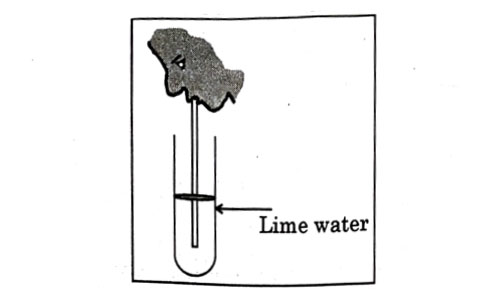
- Percentage of carbon dioxide is more in inhaled air.
- Fermentation occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Percentage of carbon dioxide is more in the exhaled air.
- Fermentation occurs in the presence of carbon dioxide.
Answer: (c)
Explanation : In the experiment it is observed that exhaled air makes the lime water milky, indicating the presence of more carbon dioxide in the exhaled air.
Question 39
If a lens can converge the sun rays at a point 20 cm. away from its optical centre, the power of this lens is –
- + 2D
- – 2D
- + 5D
- – 5D
Answer: (c)
Explanation : Power for converging/convex lens is positive.
P = = +5 D
Question 40
The radius of curvature of a converging mirror is 30 cm. At what distance from the mirror should an object be placed so as to obtain a virtual image ?
- Infinity
- 30 cm
- Between 15 cm and 30 cm
- Between 0 cm and 15 cm
Answer: (d)
Explanation : In case of concave mirror, virtual image is formed when object is placed between F and P.
Here, focal length (f) = = 15 cm
So, object should be placed between 0 cm (Pole) and 15 cm (focus).
Question 41
The length of small intestine in a deer is more as compared to the length of small intestine of a tiger. The reason for this is –
- Mode of intake of food.
- Type of food consumed.
- Presence or absence of villi in intestines.
- Presence or absence of digestive enzymes
Answer: (b)
Explanation: In herbivores like deer, length of small intestine is longer as compared to carnivores because of the food habit. Herbivores are plant eating animals and it has cellulose, which takes longer time to digest. Because of the relative difficulty with which various kinds of plant foods are broken down due to large amounts of indigestible fibers, herbivores have significantly longer gut than carnivores. The long intestine allows adequate time and space for absorption of the nutrients.
Question 42
Identify the two components of Phloem tissue that help in transportation of food in plants.
- Phloem parenchyma & sieve tubes
- Sieve tubes & companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma & companion cells
- Phloem fibres and sieve tubes
Answer: (b)
Explanation : Phloem is a complex permanent plant tissue. It is made up of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma. It helps in the transportation of the food prepared by leaves to various plant parts. It can transport food in upward as well as downward direction. Both sieve tube and companion cells are two different types of cells that are found in the phloem of angiosperms. They help in transportation of food throughout the plant.
Question 43
A converging lens from a three times magnified image od an object, which can be take on a screen. If the focal langth of the lens is 30 cm, then the distance of the object from the lens is
- -55 cm
- -50 cm
- -45cm
- -40cm
Answer: (d)
Explanation - Converging lens means convex lens
f = + 30 cm
Now, real image is always inverted
By lens formula:
Question 44
Which of the following statements is not true in reference to the diagram shown above ?
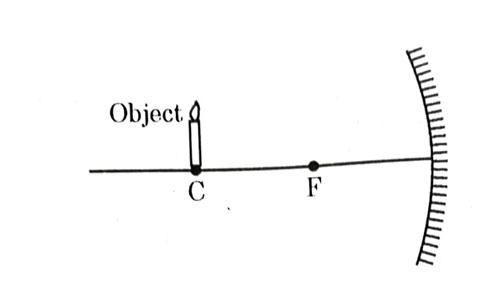
- Image formed is real.
- Image formed is enlarged.
- Image is formed at a distance equal to double the focal length.
- Image formed is inverted.
Answer: (b)
Explanation : In case of concave mirror, if object is placed at center of curvature, image is formed real, inverted, same size and at center of curvature itself. So, option (b) is false.
Question 45
In the diagram shown above n1, n2 and n3 are refractive indices of the media 1, 2 and 3 respectively. Which one of the following is true in this case ?
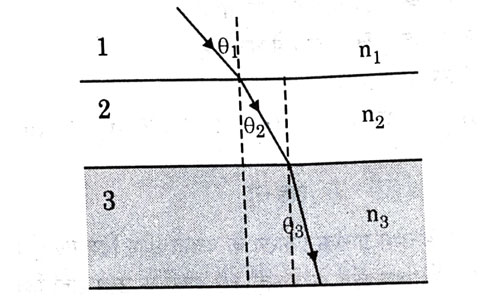
- n1 = n2
- n1 > n2
- n2 > n3
- n3 > n1
Answer: (d)
Explanation : When ray travels from medium 1 to medium 2, it bends towards normal. This is the case of light travelling from rarer to denser medium, hence
n2 > n1. Again, ray bends towards normal while traveling from medium 2 to 3. Hence, n3 > n2
Question 46
The refractive index of medium A is 1.5 and that of medium B is 1.33. If the speed of light in air is 3 x 108 m/s, what is the speed of light in medium A and B respectively ?
Answer: (d)
Explanation : As we know, Absolute refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of the velocity of light in vacuum to the velocity of light in the medium.
So,
Hence,
Similarly,
Question 47
An object of height 4 cm is kept at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of a diverging mirror. If the focal length of the mirror is 10 cm, the height of the image formed is
- + 3.0 cm
- + 2.5 cm
- + 1.0 cm
- + 0.75 cm
Answer: (c)
Explanation :
Question 48
50.0 mL of tap water was taken in a beaker. Hydrochloric acid was added drop by drop to water. The temperature and pH of the solution was noted. The following graph was obtained. Choose the correct statements related to this activity.
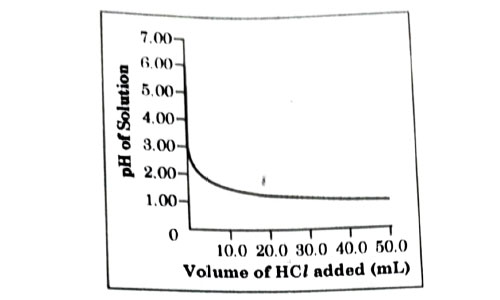
- The process of dissolving an acid in water is highly endothermic.
- The pH of the solution increases rapidly on addition of acid.
- The pH of the solution decreases rapidly on addition of acid.
- The pH of tap water was around 7.0.
- (i)and (ii)
- (i) and (iii)
- (iii) and (iv)
- (ii) and (iv)
Answer: (c)
Explanation : From the above graph, it is clear that initial pH of water is 7 but when dilute acid is added it goes down or decreases rapidly due to increase in concentration of H+.
A student, took four metals P, Q, R and S and carried out different experiments to study the properties of metals. Some of the observations were:
- All metals could not be cut with knife except metal R.
- Metal P combined with oxygen to form an oxide M2O3 which reacted with both acids and bases.
- Reaction with water.
- P – Did not react either with cold or hot water but reacted with steam
- Q – Reacted with hot water and the metal started floating
- R – Reacted violently with cold water.
- S – Did not react with water at all
Question 49
Out of the given metals, the one which needs to be stored used Kerosene is
- P
- R
- S
- Q
Answer: (b)
Explanation : Metal like sodium Na (R) is highly reactive and it should be kept in kerosene oil so that it cannot come in the contact of air to avoid explosion.
Question 50
Out of the given metals, the metal Q is
- Iron
- Zinc
- Potassium
- Magnesium
Answer: (d)
Explanation : Magnesium metal (Q) after reacting with hot water starts floating.
Question 51
Metal which forms amphoteric oxides is
- P
- Q
- R
- S
Answer: (a)
Explanation : Metal like aluminium do not react with cold or hot water but reacts with steam.
Question 52
The increasing order of the reactivity of the four metals is:
- P < Q < R
- S < R < Q
- S < P < Q
- P < R < Q
Answer: (c)
Explanation - This is as per the reactivity series.
Case-II:
The figure shown below represents a common type of dialysis called as Haemodialysis. It removes waste products from the blood. Such RB excess salts, and urea which are insufficiently removed by the kidney in patients with kidney failure. During the procedure, the patient’s blood is cleaned by filtration through a series of semi-permeable membranes before being returned to the blood of the patient. On the basis of this, answer the following questions:
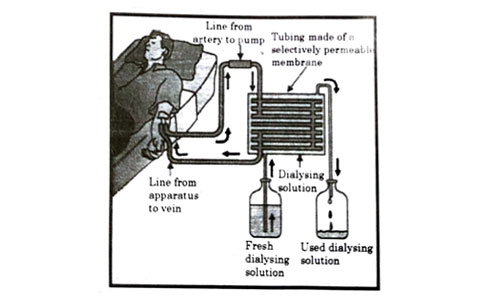
Question 53
The haemodialyzer has semi-permeable lining of tubes which help to:
- To maintain osmotic pressure of blood.
- To filter nitrogenous wastes from the dialyzing solution.
- In passing the waste product, in the dialyzing solution.
- To pump purified blood back into the body of the patient.
Answer: (c)
Explanation : The blood flows through small tubes inside the dialysis device. These are made of semipermeable membranes and are surrounded by dialysis fluid. The dialysis fluid flows in the opposite direction to the blood which is termed as counter-current flow. It helps in removal of harmful substances, waste products and excess water from the blood and gets rid of them together with the dialysis fluid.
Question 54
Which one of the following is not a function of Artificial Kidney?
- To remove nitrogenous wastes from the blood.
- To remove excess fluids from the blood.
- To reabsorb essential nutrients from the blood.
- To filter and purify the blood.
Answer: (c)
Explanation: Artificial kidney or dialysis helps in the following ways:
1. It removes wastes, excessive salt and excess water from the body, preventing their build-up.
2. Dialysis also helps to control blood pressure.
Question 55
The ‘used dialysing’ solution is rich in:
- Urea and excess salts
- Blood cells
- Lymph
- Proteins
Answer: (a)
Explanation : Artificial kidneys contain a number of tubes with a semi-permeable lining suspended in a tank filled with dialysing fluid. This fluid has the same osmotic pressure as blood, except that it is devoid of nitrogenous wastes. The patient’s blood is passed through these tubes. During this passage, the waste products from the blood pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion. The purified blood is pumped back into the patient.
Question 56
Which part of the nephron in human kidney, serves the function of reabsorption of certain substances?
- Glomerulus
- Bowmans Capsule
- Tubules
- collecting duct
Answer: (c)
Explanation : The major function of tubules is reabsorption and the process can either be through active transport or through passive transport. Also secretions by tubules help in the urine formation without affecting the electrolyte balance of the body.
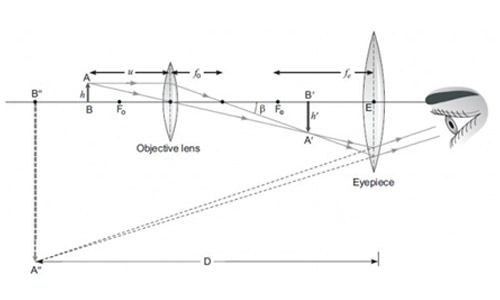
Case-III: A compound microscope is an instrument which consists of two lenses L1 and L2. The lens L1 called objective, forms a real, inverted and magnified image of the given object. This serves as the object for the second lens L2; the eye piece The eye piece function like a simple microscope or magnifier. It produces the final image, which is inverted with respect to the original object, enlarged and virtual.
Question 57
What types of lenses must be L1 and L2
- Both concave
- Both convex
- L1 - concave and L2 convex
- L1 - convex and L2 concave
Answer: (b)
Explanation – As L1 is forming real image, it must be convex lens (as concave lens cannot form real image). Also as L2 forms magnified and virtual image, it must be convex lens too (as concave lens form virtual and diminished image).
Question 58
What is the value and sign of magnification (according to the new Cartesian sign convention) of the image formed by L1?
- Value = Less than 1 and Sign = Positive
- value = More than 1 and Sign = Positive
- value = Less than 1 and Sign = Negative
- value = More than 1 and Sign = Negative
Answer: (d)
Explanation : As L1 forms real and magnified image, value is more than 1 and sign is negative as image is inverted with respect to object.
Question 59
What is the value and sign of (according to new Cartesian sign convention) magnification of the image formed by L2?
- value = Less than 1 and Sign = Positive
- value = More than 1 and Sign = Positive
- value = Less than 1 and Sign = Negative
- Value = More than 1 and Sign = Negative
Answer: (d)
Explanation : As L2 forms virtual and magnified image, value is more than 1 and sign is positive as image is erect with respect to first image (object for L2) formed by L1.
Question 60
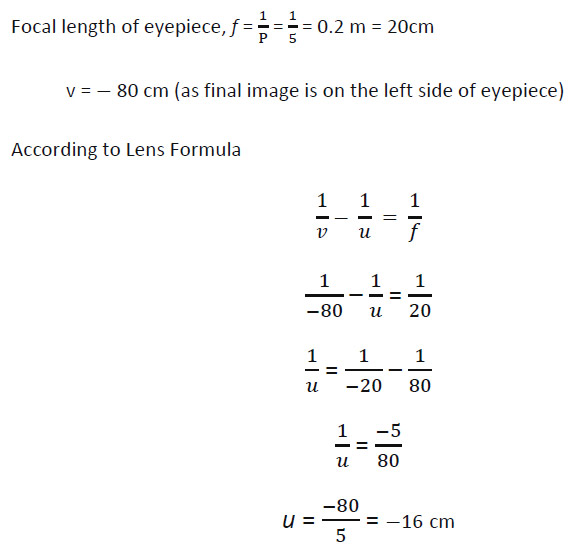
If power of the eyepiece (L2) is 5 diopters and it forms an image at a distance of 80 cm from its optical centre, at what distance should the object be?
- 12 cm
- 16 cm
- 18 cm
- 20 cm
Answer: (b)
Explanation –