Which one of the following continents has the highest growth of population:
(d) North America
Which one of the following is not an area of sparse population?
(d) Polar Regions
Which of the following is not a push factor:
(c) Medical/Educational facilities
Which one of the following is not a fact?
(c) It took 100 years for the population to rise from five billions to six billions
Name three geographical factors that influence the distribution of population.
There are a number of areas with high population density in the world. Why does this happen?
High density of population is found due to the following reasons :
What are the three components of population change?
There are three components of population change.
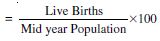
Birth rate and Death rate.
Distinguish between Push factors and Pull factors of migration.
What do you understand by ‘‘Density of population’’ ? On what factors does the density of population depend ? Give examples.
Or
Define ‘Population density’. Explain any four geographical factors that affect the distribution of population in the world.
Or
Define the term Density of population. Explain four geographical factors affecting the distribution of population in the world, with examples.
Density of Population. Density of population is a ratio between the number of people and the area of the land. Density of population is expressed as number of persons per sq. kilometre or per sq. mile.
In simple form, an average population is shown by density of population. Density of population gives a better idea of distribution of population. The density of population depends upon a number of factors—Geographical, Economic, Social and Cultural.
Write a note on Demographic Transition. State main Characteristics of each.
Or
What is demographic cycle ? Describe three stages of demographic transition theory.
Demographic Transition. Current demographic trends reveal that the annual average population increase among the developing countries is more than 20 times than that in the developed world. Although the CDR’s (Crude Death Rates) in both groups are low, the average CBRs (Crude Birth Rates) in developing countries are nearly three times more than that of the developed countries.
F.W. Notestein shows the Demographic Transition Model correlating changes in popualtion dynamics with industrialization and urbanization.