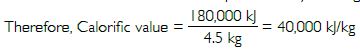Question 1:
List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer:
The three important requirements for combution to take place are:
1. Presence of a supporter of combustion i.e., oxygen
2. Presence of a combustible substance
3. Heat supply to attain the ignition temperature of the combustible substance
Question 2:
Burning of wood and coal causes _________ of air.
Answer:
Pollution
Question 3:
A liquid fuel, used in homes is _________.
Answer:
Kerosene oil
Question 4:
Fuel must be heated to its _________ _________ before it starts burning.
Answer:
Ignition temperature
Question 5:
Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by _________.
Answer:
Water
Question 6:
Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer:
CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) is a clean gaseous fuel. It has high calorific value. It burns completely in air and does not produce any harmful gases. It does not leave any residue after burning. So, pollution is reduced by the use of CNG in automobiles in our cities.
Question 7:
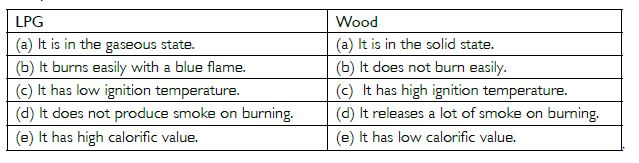
Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer:
Question 8:
Give reasons:
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer:
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because water is a good conductor of electricity. Thus, it can cause electrocution.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood because it is a cleaner fuel than wood. It neither produces smoke nor does it leave any residue after burning. It has high calorific value. While wood produces a lot of smoke on burning and leaves behind ashes on burning. Wood has low calorific value.
(c) When paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe is brought near a flame, it does not burn because the heat given to the paper gets transferred to the aluminium pipe and the ignition temperature of the paper is not attained.
Question 9:
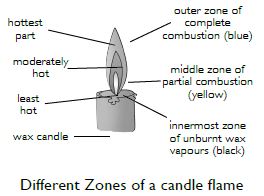
Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer:
Question 10:
Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer:
The unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed is kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg).
Question 11:
Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen and covers the combustible substance like a blanket. Thus, carbon dioxide cuts off the contact between the combustible substance and air. This extinguishes the fire.
Question 12:
It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer:
Green leaves have a lot of moisture in them which increases their ignition temperature. The dry leaves do not contain moisture and thus, their ignition temperature is low. Therefore, a heap of green leaves do not burn easily but the dry leaves catch fire easily.
Question 13:
Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer:
Goldsmith usually uses the outermost layer i.e., non-luminous zone of the flame for melting gold and silver because it is the hottest part of the flame.
Question 14:
In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer:
Mass of the fuel = 4.5 kg
Heat produced = 180,000 kJ
We know, Calorific value = Heat produced by burning 1 kg of the fuel
Question 15:
Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer:
Yes, the process of rusting can be called combustion.
Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen and gives off heat and light. Rusting of iron is also a chemical process in which iron reacts with oxygen at a very slow rate and gives off heat. So, rusting can be termed as a slow combustion process.
Question 16:
Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer:
Ramesh’s beaker will get heated in a shorter time because the outermost part of the flame is the hottest part.