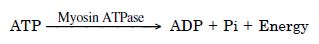Learn, study, and understand the concepts better with free NCERT Solutions at Aasoka. After deep research, these solutions are designed as per the latest CBSE syllabus. The NCERT Solutions for Class 11 are being constantly updated to include the topics as per the current guidelines. Students can take the benefit of these solutions to upgrade their performance in order to score the marks they desire. Also, the solutions are beneficial in learning time management which helps at the time of examinations.
In the chapter “Locomotion and Movement” of Class 11 Biology, students will get to learn locomotory movement, types of movement, methods of locomotion, skeletal systems, muscle contraction, favorable climatic condition, and much more.
Question 1:
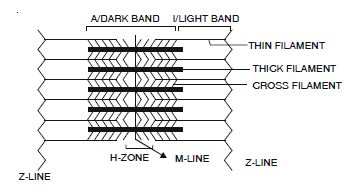
Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscles showing different regions.
Answer:
Sarcomere.
Question 2:
Define sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Answer:
According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction, the thin myofilaments slide inward toward the H-zone and thus there is a decrease in the length of the sarcomere. The cross bridges of the thick filaments come in contact with the thin filaments causing sliding of the thin filaments toward each other.
Question 3:
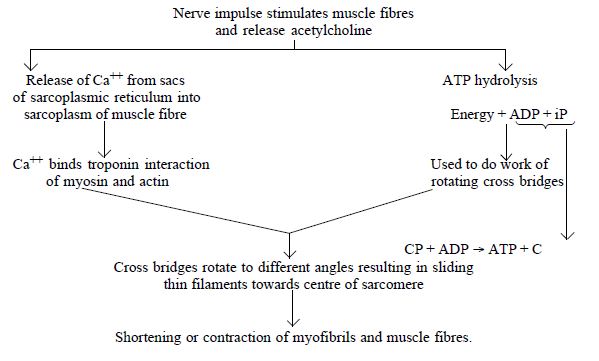
Describe the important steps in muscle contraction.
Answer:
- The signal for muscle contraction is sent by the central Nervous System via a motor neuron, by the junction called the Neuromuscular junction.
- The impulse passes from the motor end plate and stimulates the release of Ca2+ ions from sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- The Ca2+ ions cause a confirmatory change in the troponin causing exposure of active sites over the F-actin molecule due to which myosin cross-bridges are able to bind to them.
- Cross bridges get energised as :
- The energised cross bridges move causing thin filaments to slide over the thick filaments thereby causing a decrease in the length of sarcomere.
Question 4:
Actin is present in thin filament.
Answer:
TRUE
Question 5:
H-Zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments
Answer:
FALSE
Question 6:
Human skeleton has 206 bones.
Answer:
TRUE
Question 7:
There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
Answer:
FALSE
Question 8:
Sternum is present on the ventral side of
Answer:
TRUE
Question 9:
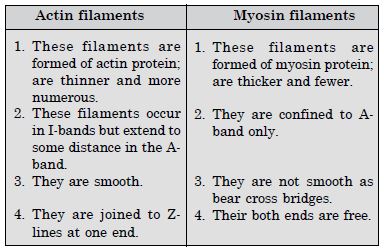
Write the differences between :
- Actin and Myosin
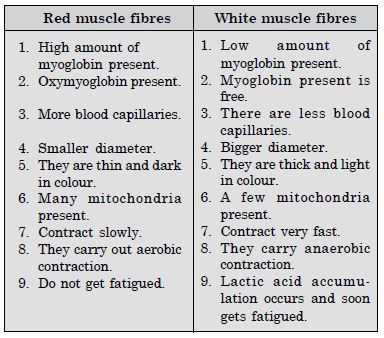
- Red and White Muscles
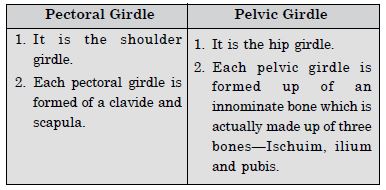
- Pectoral and Pelvic Girdle.
Answer:
- Differences between actin and myosin filaments :
- Differences between red muscle fibres and white muscle fibres
- Differences between pectoral girdle and pelvic girdle :
Question 10:
Match Column I with Column II.
(i) Smooth muscle (a) Myoglobin
(ii) Tropomyosin (b) Third class lever
(iii) Red muscle (c) Thin filament
(iv) Skull (d) Sutures
(e) Involuntary
- Smooth muscle
- Tropomyosin
- Red muscle
- Skull
Answer:
1. (b), 2. (c), 3. (a), 4. (d)
Question 11:
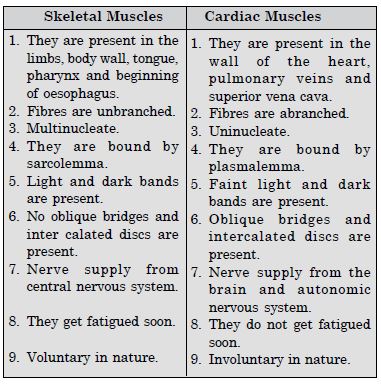
How do you distinguish between a skeletal muscle and a cardiac muscle ?
Answer:
Differences between skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles
Question 12:
What are the different types of movements exhibited by the cells of the human body ?
Answer:
The different types of movements exhibited by the cells of the human body are :
- Amoeboid Movements. These are irregular movements performed with the help of pseudopodia. These are exhibited by leucocytes of blood and macrophages of connective tissue.
- Ciliary Movements. These are performed by specialized locomotory structures called cilia. The coordinated movements of cilia in the trachea help in removal of dust particles and foreign particles inhaled with atmospheric air. Cilia also line the fallopian tubes of female, vasa efferentia of male, larynx. Passage of ova through the female reproductive tract is also facilitated by the ciliary movement.
- Muscular Movements. Such movements occur because of alternate contraction and relaxation of muscles. Such movements occur in limbs, jaws, tongue etc.
Question 13:
Name the type of joint between the following :
- Atlas/Axis
- Carpal/Metacarpal of thumb
- between phalanges.
- femur/acetabulum.
- between cranial bones.
- between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle.
Answer:
- Pivot joint
- Saddle joint
- Hinge Joint
- Ball and socket joint
- Fibrous joints
- Symphysis (Cartilaginous Joints).
Question 14:
All mammals (except few) have .................. cervical vertebra.
Answer:
seven
Question 15:
The number of phalanges in each limb of human is ..................
Answer:
Fourteen
Question 16:
Thin filament of myofibril contain 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins namely ................ and .................
Answer:
tropomyosin and troponin
Question 17:
In a muscle fibre Ca2+ is stored in..................
Answer:
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Question 18:
.................. and.................. pains of ribs are called floating ribs.
Answer:
11th and 12th
Question 19:
The human cranium is made of .................. bones.
Answer:
eight