Question 1:
How will you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane ?
Answer:
Question 2:

Answer:
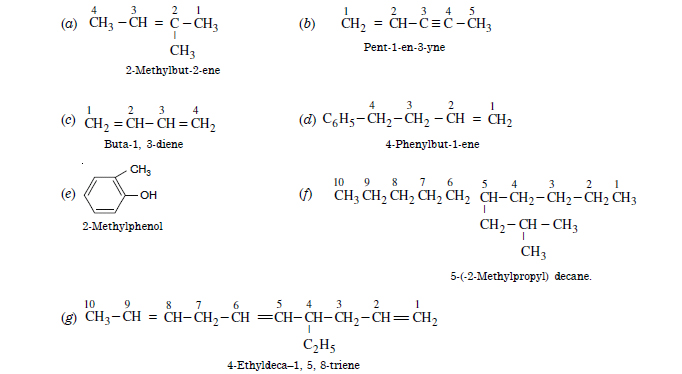
Question 3:
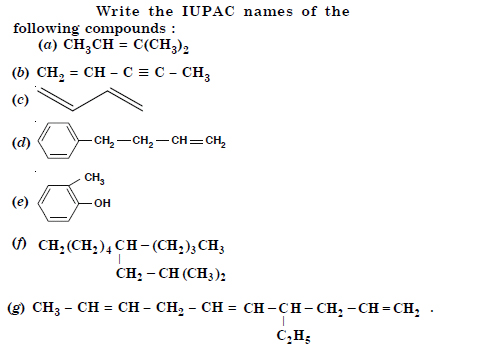
For the following compounds, write the structural formulae and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having number of double bond or triple bond as indicated. (a) C4H8 (one double bond) (b) C5H8 (one triple bond).
Answer:
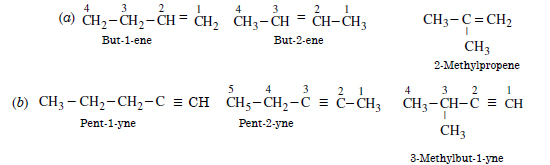
Question 4:
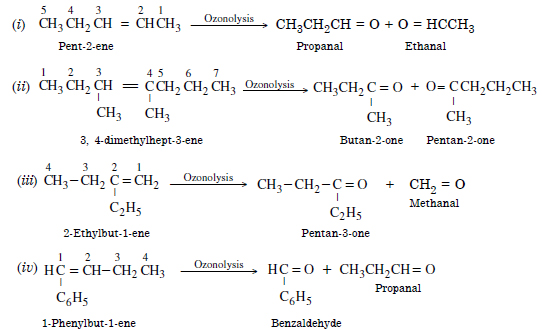
Write the IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds :
(i) Pent-2-ene
(ii)3, 4-dimethylhept-3-ene
(iii) 2-Ethylbut-1-ene
(iv) 1-Phenylbut-1-ene.
Answer:
Question 5:
An alkene ‘A’ upon ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write the structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Answer:
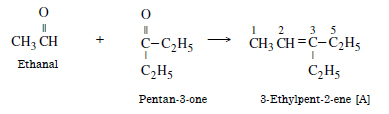
Question 6:

Answer:
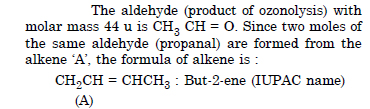
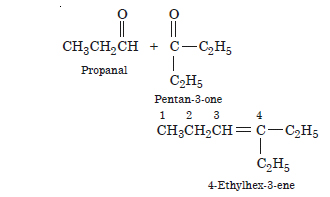
Question 7:
Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis products of an alkene. What is the structural formula of alkene ?
Answer:
Question 8:
Write the chemical equations for the combustion of the following hydrocarbons :
(a) Butane
(b) Pentene
(c) Hexyne
(d) Toluene.
Answer:
By definition, combustion is for one molecule (one mole) of the substance. The combustion equation may be written as :
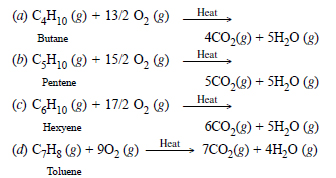
Question 9:
Draw cis and trans structures of hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher boiling point and why ?
Answer:
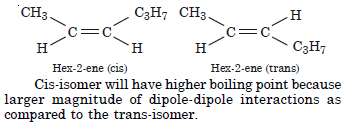
Question 10:
Why is benzene extra-ordinary stable though it contains three double bonds ?
Answer:
This is due to resonance stabilisation and due to the pesence of delocalised π-electron cloud lying above and below the plane of bonded atoms.
Question 11:
What are the necessary conditions for any compound to show aromaticity ?
Answer:
A compound is aromatic if it obeys Huckel’s rule. According to this rule :
(i) The compound should be cyclic with alternate single and double bonds with cyclic π-cloud should surround all the carbon atoms of the ring.
(ii) It should be planar.
(iii) It should contain (4n + 2) delocalised π-electrons, where n = 0, 1, 2, 3..........etc.
Question 12:
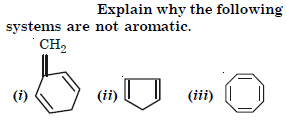
Answer:
(i) This is because it is not planar and does not obey Huckel’s rule.
(ii) This is because it is not planar and does not obey Huckel’s rule.
(iii) This is because it does not obey Huckel’s rule.
Question 13:
How will you convert benzene into
(i) p-nitrochlorobenzene
(ii) m nitrochloro-benzene
(iii) pnitrotoluene
(iv) Acetophenone ?
Answer:
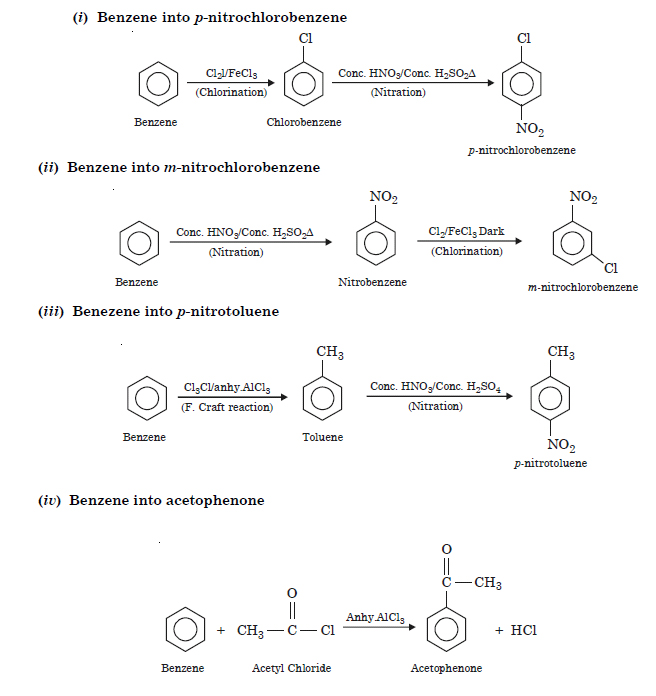
Question 14:

Answer:
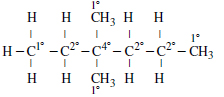
Question 15:
What is the effect of branching of alkane chain on its boiling point ?
Answer:
With the increase in branching, the surface area is decreasing, therefore, the magnitude of van der Waals forces of attraction decrease. Hence, boiling point decreases.
Question 16:
Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain with mechanism.
Answer:
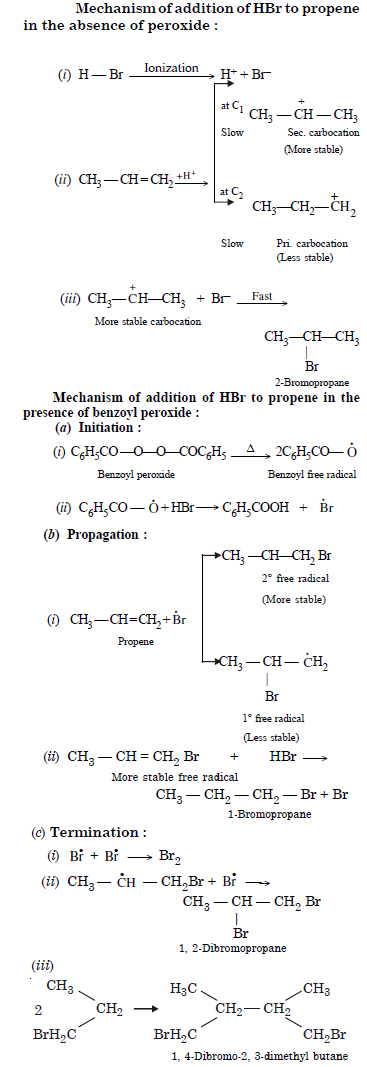
Question 17:
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethyl benzene. How does the result support Kekule’s structure of benzene?
Answer:
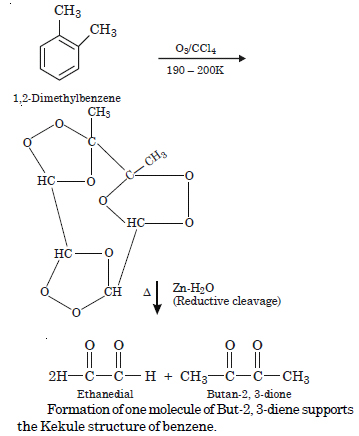
Question 18:
Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for this behaviour.
Answer:
The decreasing order of acidic nature is Acetylene > Benzene > n-Hexane. This is explained as follows : In acetylene, benzene, hexane the C-atoms are sp, sp 2 and sp 3 hybridized respectively. These orbitals have 50%, 33% and 25% s-character. Since, with the decrease in the electronegativity of the s-character of the hybrid orbital C-atoms decreases, so the tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons from the carbonhydrogen bond also decreases and the order of the acidic strength is Acetylene > Benzene > Hexane.
Question 19:
Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reaction easily and nucleophilic substitution with difficulty ?
Answer:
Benzene contains 6π-electrons and hence can undergo electrophilic substitution readily because by doing so aromatic sextet is retained. Moreover, the π-electrons in benzene are resonance stabilized and delocalized, so the nucleophilic attack is less probable and difficult.
Question 20:
How will you convert following into benzene ?
(i) Ethyne
(ii) Ethene
(iii) Hexane.
Answer:
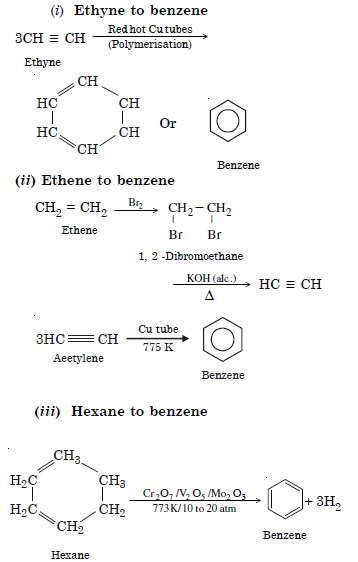
Question 21:
Write the structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2-methylbutane.
Answer:
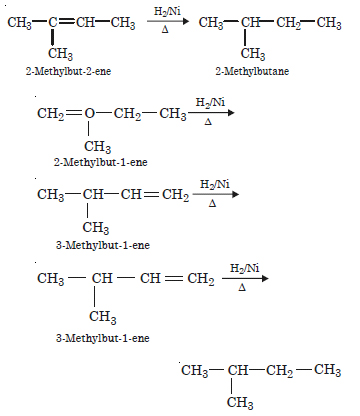
Question 22:
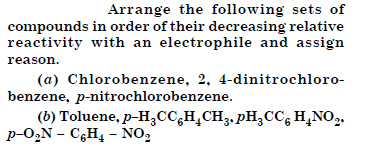
Answer:
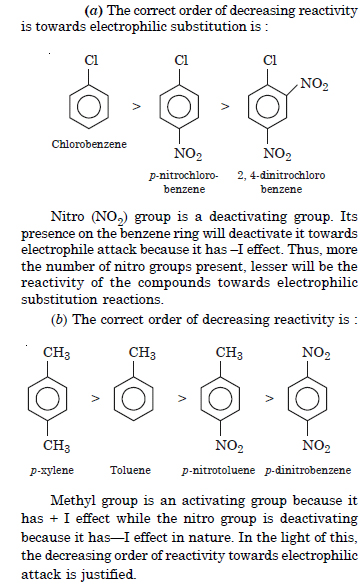
Question 23:
Out of benzene, m-dinitrobenzene and toluene, which will undergo nitration most easily and why ?
Answer:

Question 24:
Suggest the name of another Lewis acid instead of anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
Answer:
Ferric chloride (FeCl 3).
Question 25:
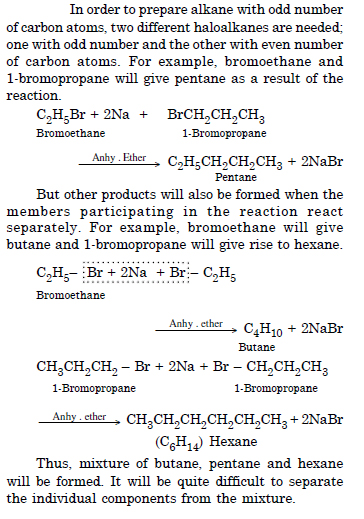
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms ? Illustrate your answer by taking an example.
Answer: