Question 1:
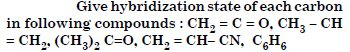
Answer:
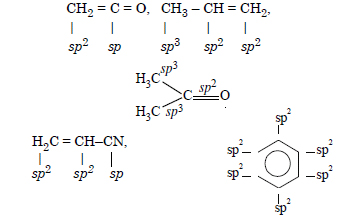
Question 2:
Answer:
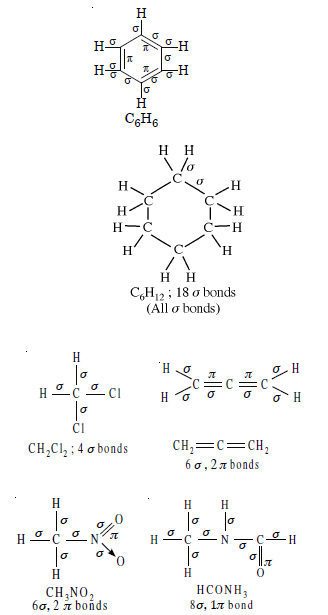
Question 3:
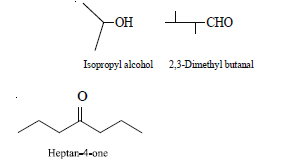
Write bondline formulae for : Isopropyl alcohol, 2, 3-Dimethyl-butanal, Heptan-4-one.
Answer:
Question 4:
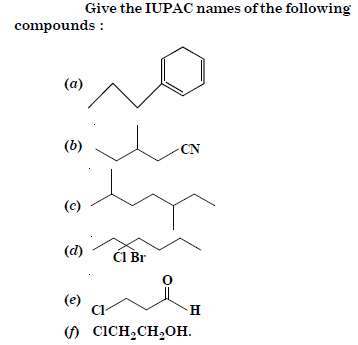
Answer:
(a) n-propyl benzene
(b) 3-Methylpentanal
(c) 2, 5-Dimethylheptane
(d) 3-Bromo-3-chloroheptane
(e) 3-Chloropropanal
(f) 2-Chloroethanol.
Question 5:
Which of the following represents the correct IUPAC name for the compounds concerned :
(a) 2, 2-Dimethylpentane or 2-Dimethylpentane,
(b) 2, 3-Dimethylpentane or 3, 4-Dimethylpentane,
(c) 2, 4, 7-Trimethy-loctane or 2, 5, 7 Trimethyloctane,
(d) 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane or 4-Chloro-2-methylpentane.
Answer:
(a) 2, 2-Dimethylpentane
(b) 2, 3-Dimethylpentane.
(c) 2, 4, 7-Trimethyloctane
(d) 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane.
Question 6:

Answer:
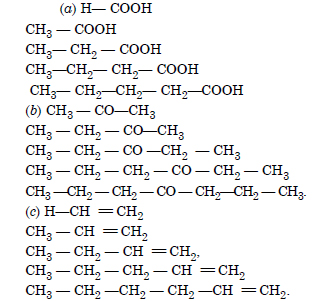
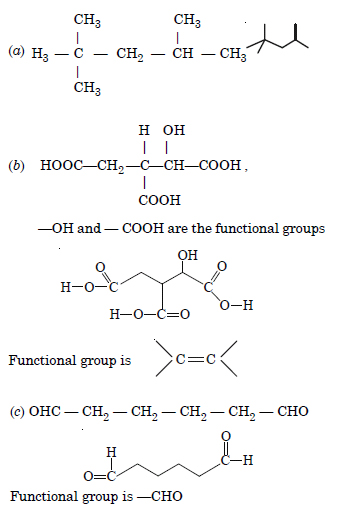
Question 7:
Give condensed and bondline structural formulae and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for :
(a) 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentane,
(b) 2-Hydroxy-1, 2, 3-propanetricarboxylic acid.
(c) Hexanedial,
Answer:
Question 8:
Answer:
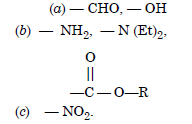
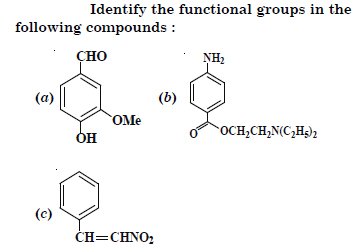
Question 9:
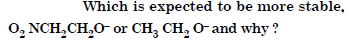
Answer:
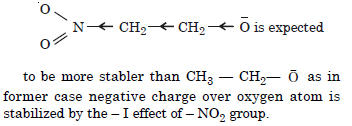
Question 10:
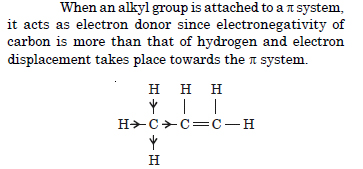
Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π system ?
Answer:
Question 11:
Answer:
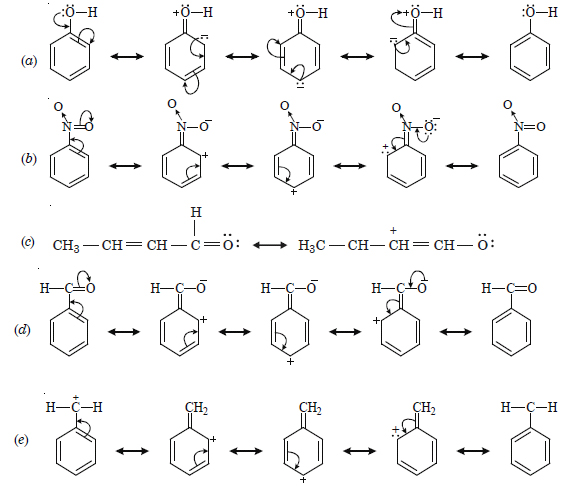
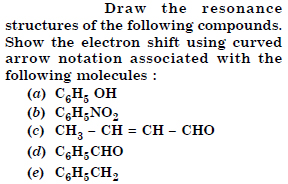
Question 12:
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles ? Explain the examples.
Answer:

Question 13:
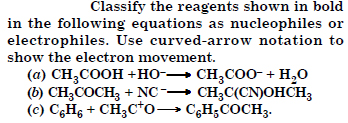
Answer:
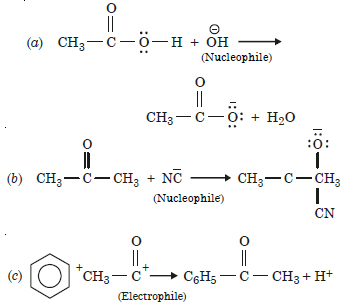
Question 14:
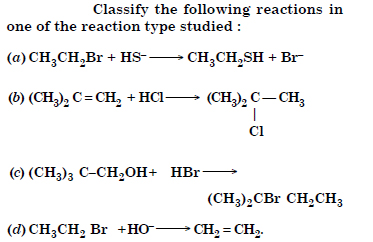
Answer:
(a) Nucleophilic substitution
(b) Electrophilic addition
(c) Nucleophilic substitution
(d) Elimination reaction.
Question 15:
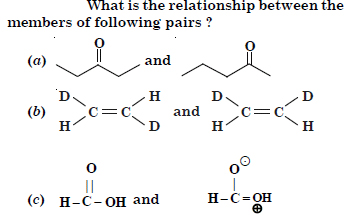
Answer:
(a) Position isomers
(b) Geometrical isomers.
(c) resonating structures
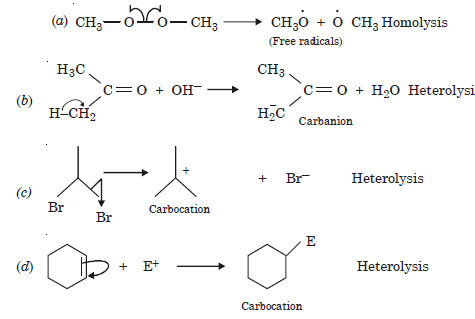
Question 16:
For the following bond cleavages, use curved arrows to show the electron flow and
classify each as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate products as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
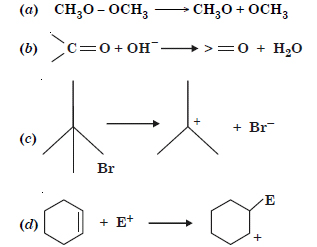
Answer:
Question 17:
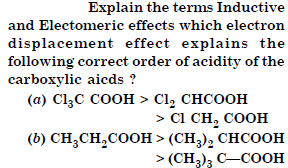
Answer:
(a) For Inductive and electromer effects refer to LAQ.Inductive effect explains the correct order of acidity of the carboxylic acids given above.
Question 18:
(a) Give a brief description of the principles of the following processes taking an example in each
case :
(i) Crystallisation
(ii) Distillation and
(iii) Chromatography.
(b) An organic compound contains 69% carbon and 4.8% hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen. Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this compound is subjected to complete combustion.
Answer:
(i) Crystallization. An isolated or prepared substance is treated with a suitable solvent in which substance is soluble while the impurities are insoluble. The pure substance is retreived from the solution by
the process of crystallization e.g. organic compounds.
(ii) Distillation. The process involves the heating of a mixture of liquids differing in nearly 40 to 60° in their boiling points. The more volatile substance vaporizes and the vapours are condensed to get a pure component e.g. alcohol and water.
(iii) Chromatography. The components of a mixture are separated on the basis of differential adsorption on a stationary phase, get adsorbed in the different regions of the stationary phase and thus get separated e.g. plant pigments.
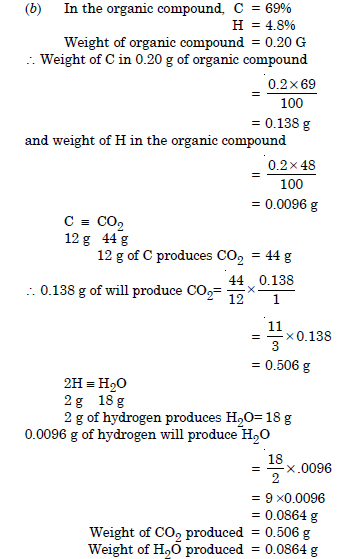
Question 19:
Describe the method, which can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in a solvent S.
Answer:
Two substances soluble in a solvent S having different solubilities can be separated by fractional crystallization. The solution containing two compounds is heated to concentrate and saturated solution at high temperature on cooling undergoes crystallization, separating lesser soluble component first which is removed followed by the separation of the 2nd component subsequently.
Question 20:
What is the difference between distillation, distillation under reduced pressure and steam distillation ?
Answer:
Distillation involves the separation of ordinary liquids which differ from each other in their boiling point by 40-50°C by heating in a retort. Distillation under reduced pressure is applicable to the compounds which decompose before reaching their boiling point, on reducing the pressure over the liquid surface the boiling point of the liquid gets lowered. In this method distillation is carried out under reduced pressure. Steam distillation is applicable to those substances, which are immiscible with water but volatile in steam. In this case distillation is carried out with the help of steam.
Question 21:
Discuss the chemistry of Lassaigne’s test.
Answer:
While preparing Lassaigne’s test the organic compound decomposes and the elements of the organic
compound combine with sodium metal to form water soluble sodium salts e.g.
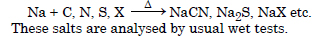
Question 22:
Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an organic com-pound by
(i) Duma’s method and
(ii) Kjeldahl’s method.
Answer:
compound is heated strongly in a combustion tube in a furnace when nitrogen present in the organic compound is released as free nitrogen collected under KOH solution. From the volume of N2 gas collected at STP the percentage of Nitrogen could be determined. (ii) Kjeldahl’s method. A known mass of an organic compound is digested with conc. H2SO4 for 2, 3 hours when nitrogen present in the organic compound is converted isnto Amm. Sulphate which when heated with concentrated (40%) KOH, liberates NH3 gas which is absorbed in the known volume of a standard acid. The volume of the unconsumed (unneutralized) acid is found out volumetrically. Thus the volume of the acid neutralized by ammonia is determined with the help of which the percentage of nitrogen in the given organic compound is calculated.
Question 23:
Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens, sulphur and phosphorus present in an organic compound.
Answer:
(a) Estimation of halogens : The halogens present in an organic compound can be estimated by Carius method. In this method, a small known weight of the given organic compound is heated with fuming HNO3 and
AgNO3 in a Carius tube for 3-4 hours in a sealed tube with the help of electric furnace. The halogen present
in an organic compound gets precipitated as silver halide. The precipitate of silver halide is separated by filtration, washed, dried and weighed. From this data we can calculate the percentage of halogen in the organic compound.

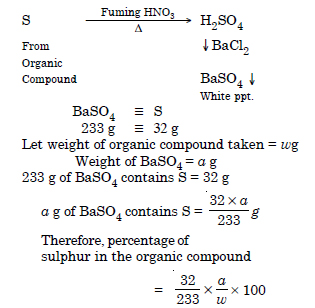
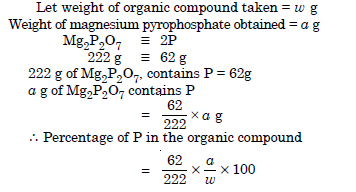
Question 24:
Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Answer:
Paper chromatography : It is a type of partition chromatography. In this case, a special quality paper known as chromatography paper is used. This paper contains water trapped in it which acts as a stationary phase. A spot of solution of the mixture is applied at the base of the chromatography paper. This paper is suspended in a suitable solvent which acts as a mobile phase. The solvent rises up the paper by capillary action and flows over the spot. This paper selectively retains different components according to their different partition in the two phases. The paper strip so developed is called chromatogram. The spots of the colourless compounds may be observed either under ultraviolet light or using a suitable spraying agent. For example, amino acids may be detected by spraying ninhydrin solution.
Question 25:
Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrate for testing halogens ?
Answer:
If the organic compound contained nitrogen or sulphur, they from NaCN, Na2S in the Lassaigne’s extract which may form white and black ppt. due to AgCN and Ag2S, which interferes in the detection of elements. On boiling with conc. HNO3, NaCN and Na2S decompose releasing HCN, H2S vapours. Now Ag NO3 will give the precipitate of AgX only.
Question 26:
Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound fused with sodium for testing nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus.
Answer:
In order to test for elements in an organic compound, it is fused with molten sodium metal because at high temperature the organic compound decomposes and the elements like N, S, P combine with sodium metal to form water soluble salts, which could be detected with the help of usual wet tests.
Question 27:
Name a suitable technique of separation of components from a mixture of calcium sulphate and camphor.
Answer:
Camphor is volatile while CaSO4 is not, therefore the two components could be separated by the technique of sublimation.
Question 28:
Explain why an organic liquid vaporizes at a temperature below its boiling point in its steam distillation.
Answer:
During steam distillation an organic compound vaporizes along with the steam and the sum of the partial vapour pressures of the organic compound (pcomp.) and that of water ( H2O p ) becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure P. P = H2O p + pcomp. Therefore the organic substance vaporizes below its normal boiling point.
Question 29:
Will CCl4 give white precipitate of AgCl on heating it with silver nitrate ? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
CCl4 does not give white ppt of AgCl with AgNO3 because it does not furnish free chloride ions in the solution due to strong C—Cl bonds.
Question 30:
Why is a solution of KOH used to absorb CO2 evolved during the estimation of ‘C’ present in an organic compound ?
Answer:
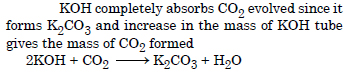
Question 30:
Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acidification of sodium extract for testing sulphur by lead acetate test ?
Answer:
For testing sulphur from sodium extract, it is acidified with acetic acid because sulphuric acid gives white precipitate with lead acetate solution even if sulphur is absent.
Question 31:
An organic compound contains 69% carbon and 4.8% hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen. Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this substance is subjected to complete combustion.
Answer:

Question 32:
A sample 0.5 g of an organic compound was treated according to Kjeldahl’s method. The ammonia evolved was absorbed in 50 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4. The residual acid required 60 mL of 0.5 M solution of NaOH for neutralization. Find the percentage of nitrogen in the compound.
Answer:
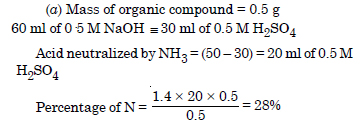
Question 33:
0.3780 g of an organic compound gave 0.5740 g of silver chloride in Carius estimation. Calculate the percentage of chlorine in the compound.
Answer:
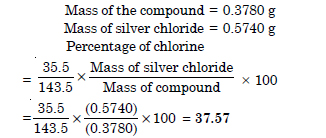
Question 34:
In an estimation of sulphur by Carius method, 0.468 of an organic sulphur compound gave 0.668 g of barium sulphate. Find the percentage of sulphur in the compound.
Answer:
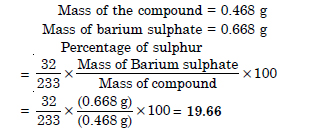
Question 35:
In the organic compound CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH2 – C≡CH, the C2–C3 bond is formed by the interaction of a pair of hybridised orbitals :
Answer:
sp – sp3
Question 36:
In the Lassaigne’s test for nitrogen in an organic compound, the Prussian blue colour is obtained due to the formation of :
Answer:
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Question 37:
Which of the following carbocation is most stable ?
Answer:
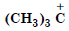
Question 38:
The best and latest technique for isolation, purification and separation of organic compounds is :
Answer:
Chromatography.
Question 39:
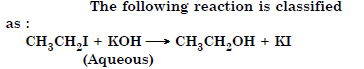
Answer:
nucleophilic substitution
