Question 1:
Discuss the pattern of variation in oxidation states of :
(i) B to Tl
(ii) C to Pb.
Answer:

Question 2:
How can you explain higher stability of BCl3 as compared to TlCl3 ?
Answer:
This is due to inert pair effect. Inert pair effect is more in Tl and negligible in case of B.
Question 3:
Why does BF3 behave as Lewis acid ?
Answer:
BF3 behaves a Lewis acid because in BF3 the central boron atom has only six electrons in its valence shell after sharing with the electrons of the F atoms. It is an electron deficient compound and, therefore, behaves as a Lewis acid.
Question 4:
Consider the compounds BCl3 and CCl4. How will they behave towards water ?
Answer:
In BCl3 (B atom is sp2 hybridised), the B atom has incomplete octet and has an unhybridised 2p-orbital which can take up electron pair from the H2O molecule to form addition product.
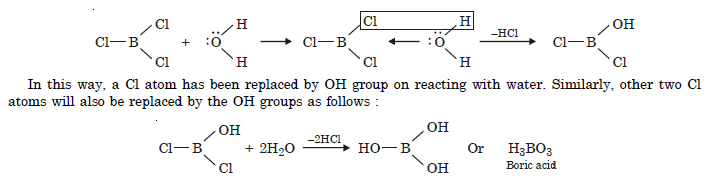
Question 5:
Is boric acid a proton acid ? Explain.
Answer:
Boric acid is not a proton acid. It is a Lewis acid and accepts electron pair from hydroxyl group of H2O molecule.

Question 6:
Explain what happens when boric acid is heated ?
Answer:
The smog is a combination of smoke and fog. The difference between classical and photochemical smogs are as follows :
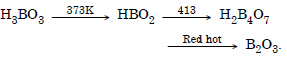
Question 7:
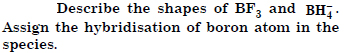
Answer:
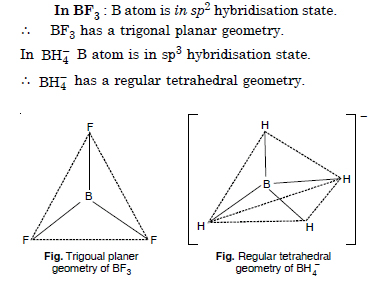
Question 8:
Write reactions to justify amphoteric nature of aluminium.
Answer:
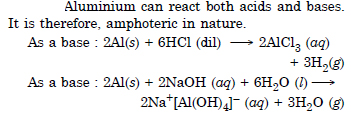
Question 9:
What are electron deficient compounds ? Are BCl3 and SiCl4 electron deficient species ? Explain.
Answer:
Electron deficient compounds are the compounds in which the central atom in their molecule has a tendency to take up electron pairs. The electron deficient compounds are also called Lewis acids. Yes, both BCl3 and SiCl4 are electron deficient. Whereas B atom has a vacant 2p orbital atom at the same time Si has vacant 3d-orbitals. Both these atoms can take up electron pair from electrons donor species.
Question 10:

Answer:
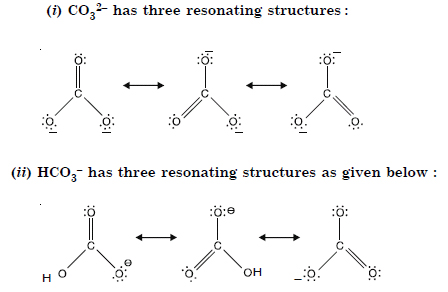
Question 11:

Answer:
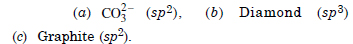
Question 12:
Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on basis of their structures.
Answer:
Refer to Additional Important Qs. (SAQs); Q. No. 42.
Question 13:
Rationalise the given statements and give chemical reaction :
(a) lead (II) chloride reacts with Cl2 to give PbCl4.
(b) lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat
(c) lead is known not to form an iodide, PbI4.
Answer:

Question 14:
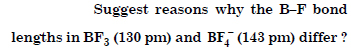
Answer:
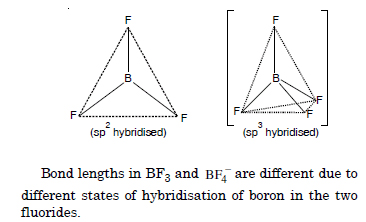
Question 15:
If B – Cl bond has a dipole moment, why does BCl3 have zero dipole moment ?
Answer:
B–Cl bond has a certain dipole moment because it is of polar nature. But BCl3 has zero dipole moment since the molecule is symmetrical (trigonal planar) in which net dipole moment is zero.
Question 16:
Aluminium trifluoride is insoluble in anhydrous HF but dissolves on addition of NaF. Aluminium trifluoride precipitates out of the resulting solution when gaseous BF3 is bubbled through. Give reasons.
Answer:

Question 17:
Suggest a reason as to why CO is poisonous in nature.
Answer:
Carbon monoxide is highly poisonous in nature. Its poisonous character is due to tendency to combine with haemoglobin present in blood to form carboxyhaemoglobin due to which haemoglobin is not in a position to carry the oxygen to different parts in the body. This will lead to suffocation and ultimately to death.
Question 18:
How is excess content of CO2 responsible for global warming ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) like methane has a tendency to absorb heat. It is known as a green house gas and its high concentration in the atmosphere is responsible for global warming.
Question 19:
Explain the structure of diborane and boric acid.
Answer:
Refer to Additional Important Qs. (SAQs); Q. No. 30.
Question 20:
What happens when
(a) Borax is heated strongly
(b) Boric acid is added to water
(c) Aluminium is treated with dilute Na
(d) BF3 is reacted with ammonia.
Answer:
(a) When powdered borax is heated strongly in the flame of bunsen burner, it forms colourless transparent glassy (glass-like) bead made of sodium meta borate and boric anhydride
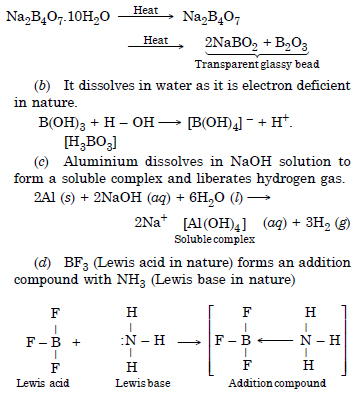
Question 21:
Explain the following reactions :
(a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper.
(b) Silicon dioxide is treated with hydrogen fluoride
(c) CO is heated with ZnO
(d) Hydrated alumina is treated with aqueous NaOH solution.
Answer:
(a) When powdered borax is heated strongly in the flame of bunsen burner, it forms colourless transparent glassy (glass-like) bead made of sodium meta borate and boric anhydride

Question 22:
Give reasons :
(i) Conc. HNO3 can be transported in aluminium container.
(ii) Graphite is used as lubricant.
(iii) Diamond is used as an abrasive.
(iv) Aluminium alloys are used to make aircraft body.
(v) Aluminium utensils should not be kept in water overnight.
(vi) Aluminium wire is used to make transmission cables.
Answer:
(i) Conc. HNO3 initially reacts with aluminium to form aluminium oxide (Al2O3) which
forms a thin protective coating inside the container. The metal becomes passive and does not further with the acid any more. Therefore, the acid can be safely stored in aluminium container.
(ii) Graphite is used as lubricant because of its soft and greasy nature. This is probably due to the presence of layers in the arrangement of carbon atoms in graphite which can readily slip over each other.
(iii) Diamond is used as an abrasive because of its extremely hard nature due to the pressure of strong C – C bonds.
(iv) Alloys of aluminium ; Magnalium and Duralumin both of which contain about 95% of the metal are used for making aircraft body because these
are light and tough.
(v) Although the metal as such is not affected by water, but when kept overnight it may be slowly affected by moisture in the presence of oxygen (air.)
(vi) The metal is not affected by air and moisture and also because of its good conductivity, it is used to make transmission cables.
Question 23:
Explain why is there a phenomenal decrease in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon.
Answer:
On moving from B to Sn, the ionisation enthalpy decreases. But from Sn to Pb, there is a slight increase in ionization enthalpy due to poor shielding effect of intervening d and f-orbitals.
Question 24:
How would you explain the lower atomic radius of Ga as compared to Al ?
Answer:
Atomic radius of Ga is less than Al because of poor shielding by intervening 3d electrons.
Question 25:
What are allotropes ? Sketch the structure of two allotropes of carbon namely diamond and graphite. What is the impact of structure on physical properties of two allotropes ?
Answer:
Refer to Additional Important Qs.(SAQs); Q. No. 7.
Question 26:
Classify following oxides as neutral, acidic, basic or amphoteric : CO, B2O3, SiO2, CO2, Al2O3, PbO2, Tl2O3.
Answer:
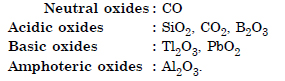
Question 27:
In some of the reactions thallium resembles aluminium, whereas in others it resembles with group I metals. Support this statement by giving some evidences.
Answer:
Aluminium (Al) generally exhibits +3 oxidation state in its compounds. Thallium (Tl), the last member of the group 13, is expected to show oxidation states of + 3 and + 1 (due to inert pair effect). Thus, the metals resemble in the reactions involving + 3 oxidation state. However, they differ with respect to + 1 oxidation state.
Question 28:
When metal X is treated with sodium hydroxide, a white precipitate
(A) is obtained which is soluble in excess of NaOH to give soluble complex
(B). Compound (A) is soluble in dilute HCl to form compound
(C). The compound (A) when heated strongly gives
(D) which is used to extract metal. Identify (X), (A), (B), (C) and (D). Write suitable equations to support their identities.
Answer:

Question 27:
What do you understand by (a) inert pair effect (b) allotropy (c) catenation ?
Answer:
(a) Inert Pair effect. The reluctance of ns2 pair in p-block elements having higher atomic number to take part in bond formation is called inert pair effect.
(b) Allotrops : The existence of an element in more than one form having different physical properties but same or slightly different properties is called allotropy.
(c) Catenation : The property by virtue of which a large number of atoms of the same element get linked together through covalent bonds resulting in the formation of long chains, branched chains and rings of different sizes is called catenation.
Question 28:
A certain salt X, gives the following results :
(i) Its aqueous solution is alkaline to litmus.
(ii) It swells up to a glassy material Y on strong heating.
(iii) When conc. H2SO4 is added to a hot solution of X, white crystal of an acid Z separates out. Write equations for all the above reactions and identify X, Y and Z.
Answer:
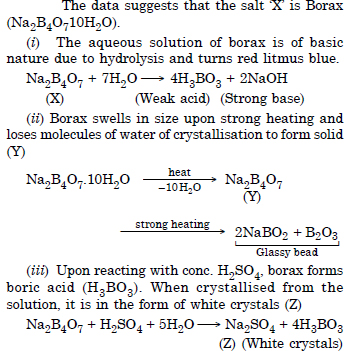
Question 29:
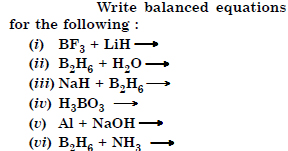
Answer:
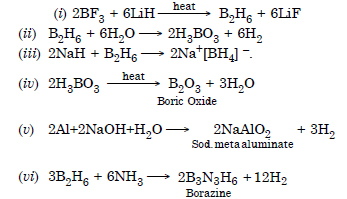
Question 30:
Give one method for industrial preparation and one for laboratory preparation of CO and CO2 each.
Answer:
Refer to Additional Important Qs.(LAQs); No. 13.
Question 31:
An aqueous solution of borax is
Answer:
(c).
Question 32:
Boric acid is polymeric due to
Answer:
(b).
Question 33:
The type of hybridisation of boron in diborane is
Answer:
(c).
Question 34:
Thermodynamically the most stable form of carbon is
Answer:
(b).
Question 35:
Elements of group 14
Answer:
(b).
Question 36:
If the starting material for the manufacture of silicones is RSiCl3, write the structure of the product formed.
Answer:

