Question 1:
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30º C ?
Answer:
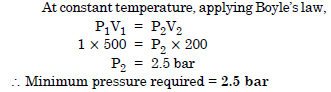
Question 2:
A vessel of 120 ml capacity contains a certain amount of gas at 35°C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is transferred to another vessel of volume 180 ml at 35°C. What would be its pressure ?
Answer:
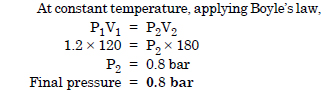
Question 3:
Using the equation of state PV = nRT; show that at a given temperature density of a gas is proportional to gas pressure.
Answer:
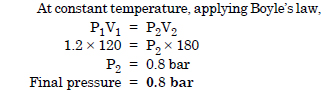
Question 4:
At 0°C, the density of a gaseous oxide at 2 bar is same as that of nitrogen at 5 bar. What is the molar mass of the oxide ?
Answer:
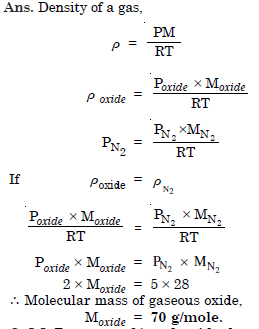
Question 5:
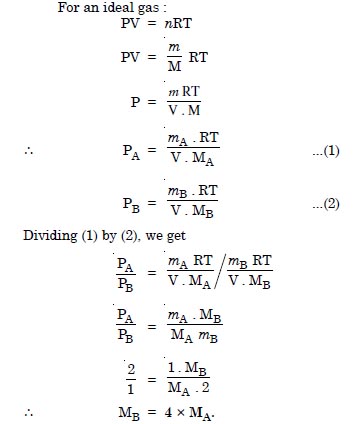
Pressure of 1 g of an ideal gas A at 27°C is found to be 2 bar. When 2 g of another ideal gas B is introduced in the same flask at same temperature, the pressure becomes 3 bar. Find a relationship between their molecular masses.
Answer:
Question 6:
The drain cleaner Drainex contains small bits of aluminium which reacts with caustic soda to produce hydrogen. What volume of hydrogen at 20°C and one bar will be released when 0.15 g of aluminium reacts ?
Answer:

Question 7:
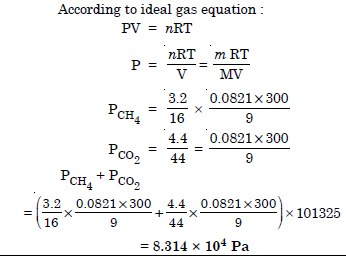
What will be the pressure exerted by a mixture of 3.2 g of methane and 4.4 g of carbon dioxide contained in a 9 dm3 flask at 27° C ?
Answer:
Question 8:
What will be the pressure of the gas mixture when 0.5 L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0 L of oxygen at 0.7 bar are introduced in 1L vessel at 27°C ?
Answer:
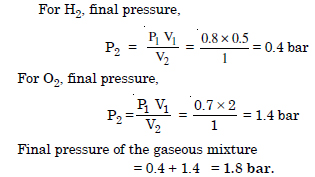
Question 9:
Density of a gas is found to be 5.46 g/dm3 at 27°C and 2 bar pressure. What will be its density at S.T.P. ?
Answer:

Question 10:
340.05 ml of phosphorus vapours weigh 0.0625 g at 546°C and 0.1 bar pressure. What is the molar mass of phosphorus ?
Answer:
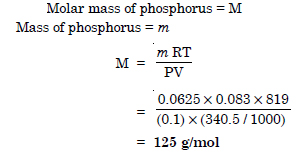
Question 11:
A student forgot to add the reaction mixture to the round bottomed flask at 27°C but put it on the flame. After a lapse of time, he realised his mistake using a pyrometer he found the temperature of flask was 477°C. What fraction of air would have been expelled out ?
Answer:

Question 12:
Calculate the temperature of 4.0 moles of a gas occupying 5 dm3 at 3.32 bar (R = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1)
Answer:
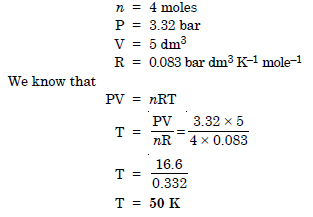
Question 13:
Calculate the total number of electrons present in 1.4 g of nitrogen gas.
Answer:
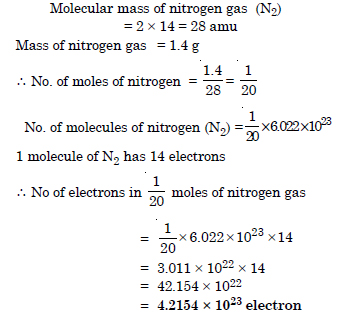
Question 14:
How much time would it take to distribute one Avogadro number of wheat grains, if 1010 grains are distributed each second ?
Answer:
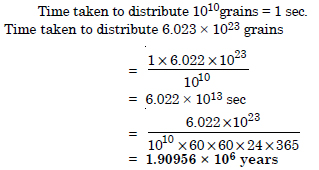
Question 15:
Calculate the total pressure in a mixture of 8 g of oxygen and 4 g hydrogen, confined in a vessel of 1 dm3 at 27°C. R = 0.083 bar dm3 k–1 mol–1
Answer:
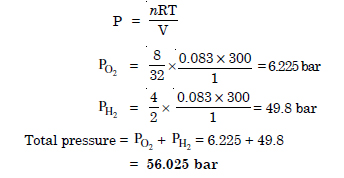
Question 16:
Pay load is defined as the difference between the mass of displaced air and the mass of balloon. Calculate the pay load when a balloon of radius 10 m, mass 100 kg is filled with helium at 1.66 bar at 27°C. (Density of air = 1.2 kg m–3 and R = 0.083 bar dm3 K–1 mol–1).
Answer:

Question 17:
Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1°C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar L K–1 mol–1
Answer:
T = 31.1°C = 273 + 31.1 = 304.1 K
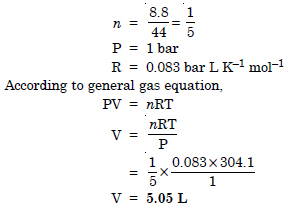
Question 18:
2.9 g of a gas at 95°C occupies the same volume as 0.184 g of hydrogen at 17°C at the same pressure. What is the molar mass of the gas ?
Answer:
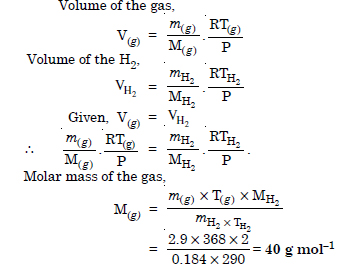
Question 19:
A mixture of hydrogen and oxygen at one bar pressure contains 20% by weight of hydrogen. Calculate the partial pressure of hydrogen.
Answer:
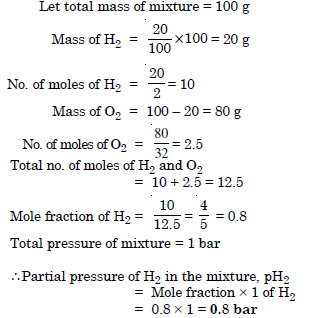
Question 20:
What would be the SI unit for the quantity PV2T2/n ?
Answer:
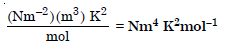
Question 21:
In terms of Charles’s law explain why – 273°C is the lowest possible temperature.
Answer:
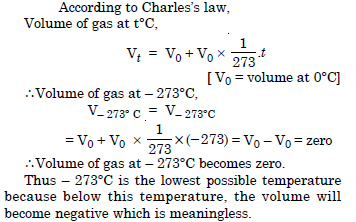
Question 22:
Critical temperature for carbon dioxide and methane are 31.1° C and – 81.9° C respectively. Which of these has stronger intermolecular forces and why ?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, because of the presence of weak π-bonds.
Question 23:
Explain the physical significance of van der Waals’ constants.
Answer:
van der Waals’ constant ‘a’ is a measure of the magnitude of the attractive forces among the molecules of a gas, while constant ‘b’ is a measure of effective size of the gas molecules.
