Time flies before you even realize it. So, get started with your exam preparation now with free NCERT Solutions at Aasoka. Designed in accordance with the latest CBSE syllabus, these solutions provide important questions along with their solutions to help students score good grades. Start practicing with top NCERT Solutions for Class 11 to enhance your overall performance.
“Secularism” chapter of Class 11 Political Science teaches western and Indian approaches to secularism, the idea of secularism, Kemal Ataturk’s Secularism, what is a secular state, the role of religious denominations, rationale and criticisms of Indian secularism; the secular nature of the state, and much more.
Question 1:
Which of the following do you feel are compatible with the idea of Secularism ? Give reasons.
- Absence of domination of one religious group by another.
- Recognition of a State religion.
- Equal State support to all religions.
- Mandatory prayers in schools.
- Allowing separate educational institutions for any minority community.
- Appointment of temple management bodies by the government.
- Intervention of State to ensure entry of Dalits in temples.
Answer:
- It is compatible with the idea of Secularism because Secularism opposes all forms of inter-religious domination.
- It is not compatible with Secularism because in a Secular State, there is no official religion.
- It is compatible with Secularism because in Secularism, all religions are treated alike.
- It is not compatible with Secularism.
- It is compatible with Secularism because in Secularism, minority community should be given freedom to run their schools.
- It is not compatible with Secularism because government should not interfere in the temple management.
- It is compatible with Secularism. All Hindus including Dalits should be free to enter temples.
Question 2:
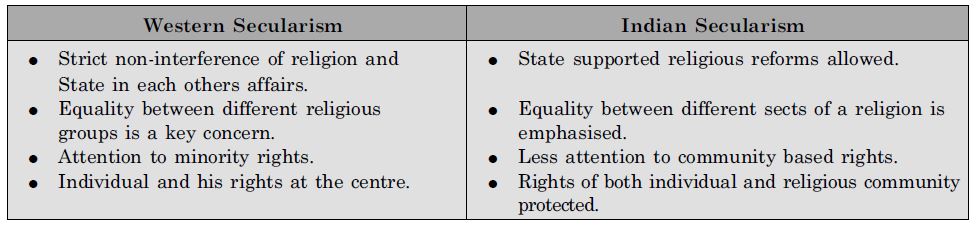
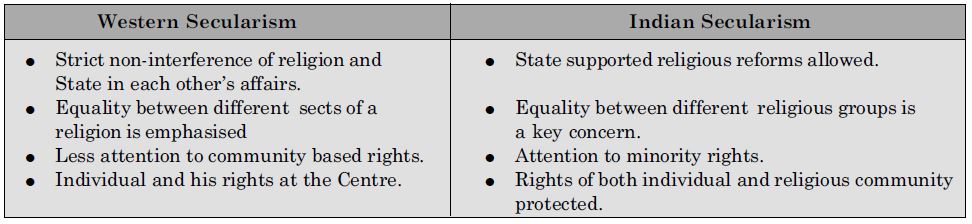
Some of the key characteristics of Western and Indian model of Secularism have got mixed up. Separate them and make a new table.
Answer:
Question 3:
What do you understand by Secularism?
Can it be equated with religious tolerance?
Answer:
The dictionary meaning of Secularism is
“Indifference or rejection or exclusion of religion and
religious considerations”. Secularism rejects religion
completely. It rather supports anti-religious feelings.
Secularism implies a way of life and conduct guided
purely by materialistic consideration. It holds that
materialism alone benefits mankind while religious
feelings retard it. But in its modern meaning, Secularism
means freedom of religion and a non-interference policy
of state in religious activity. In this way, Secularism in
its modern meaning is not anti-religious. It is this policy
of non-interference by the State which gives equal
protection to all the religions. Secularism is a doctrine
that opposes all forms of inter-religious domination.
Secularism challenges not merely inter-religious but
also intra-religious domination.
According to Encyclopedia Britannica, “The term
Secular means non-spiritual, having no concern with
religious or spiritual matters.”
According to Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, “Secularism does
not mean that we shall not take into consideration the
religious sentiments of the people. All that what a
Secular State means is that Parliament shall not be
competent to impose any particular religion on the rest
of the people.”
Can Secularism be equated with religious
tolerance ? No doubt religious tolerance is needed for
the establishment of Secularism. But Secularism cannot
be equated with religious toleration because Secularism
is much more than the mere peaceful co-existence or
toleration.
Question 4:
Do you agree with the following statements ? Give reasons for supporting or opposing any of them.
- Secularism does not allow us to have a religious identity.
- Secularism is against inequality within a religious group or between different religious groups.
- Secularism has a western-Christian origin. It is not suitable for India.
Answer:
- We don’t agree with this statement because Secularism allows religious identity. In Secularism, people enjoy freedom of religion.
- We agree with this statement because Secularism is against inequality within a religious group or between different religious groups. In Secularism, all religions are treated equal and no discrimination is made on the basis of religion.
- We don’t agree with this statement. The Western model of Secularism is not a product of the Christian world. Secularism is suitable to Indian conditions.
Question 5:
‘Indian Secularism focuses on more than the religion-state separation.’ Explain.
Answer:
India is a Secular State. Secularism is a basic
feature of the Indian Constitution. Sometimes it is said
that Indian Secularism is an imitation of Western
Secularism. But it is not a reality. Indian Secularism
is basically different from Western Secularism. In
Western Secularism, emphasis is on separation of State
from the Church. But the Indian Secularism focuses on
more than religion-state separation. In India, there was
a culture of inter-religious toleration. Western modernity
and thought influences Indian culture. Western
modernity emphasised on equality within the
community. Idea of inter-community equality replaced
the notion of hierarchy. Moreover, Indian Secularism
opposed the oppression of Dalits and Women within
Hinduism, and the discrimination against women
within Islam or Christianity.
Western Secularism deals with freedom of
individuals, whereas Indian Secularism deals with
rights of the minorities also. Article 26 of the Indian
Constitution provides that subject to public order,
morality and health, every religious denomination
shall have the right (I) to establish and maintain
institutions for religious and charitable purposes;
(II) to manage its own affairs in matters of religion;
(III) to own and acquire movable and immovable
property; and (IV) to administer such property in
accordance with the law. Indian Secularism has
supported religious reform by the State. Untouchability
is abolished by the Indian Constitution. Many religious
reform Acts have been passed by the Indian
Parliament. Thus, Indian Secularism focuses on more
than the religion-state separation.
Question 6:
Explain the concept of principled distance.
Answer:
In Secularism, the concept of principled distance means that the state should not interfere in any religion actively. After the First World War, Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, ruler of Turkey, instead of following concept of distance, followed active intervention in suppression of religion.