Question 1:
Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer:
Robert Hooke (1665) discovered cells. He was examining a thin slice of cork under a microscope when he noticed that the thin slice of cork resembled the structure of a honey comb consisting of many hexagonal compartments. He called these boxes as ‘cells’.
Question 2:
Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer:
All metabolic activities of life such as respiration, digestion, excretion and reproduction take place at the cellular level. Cells contain genetic materials, which play an important role in the transfer of hereditary characters from parents to offspring. Cells of multicellular organisms are grouped to form tissues, which are further organised to form organs. Organs, in turn, form organ systems and organ systems work together to form what an organism is in its totality. Thus, cells are the basic building structural and functional units of life.
Question 3:
How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
Substances such as carbon dioxide move in and out of cells by the process of diffusion. In this process, there is a spontaneous movement of substances from a region of higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration. Movement of water occurs by the process of osmosis. In this process, there is spontaneous movement of water from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration across a selectively permeable membrane.
Question 4:
Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
Plasma membrane permits the entry and exit of selected materials in and out of the cell. It also prevents movement of some other materials. Hence, it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Question 5:
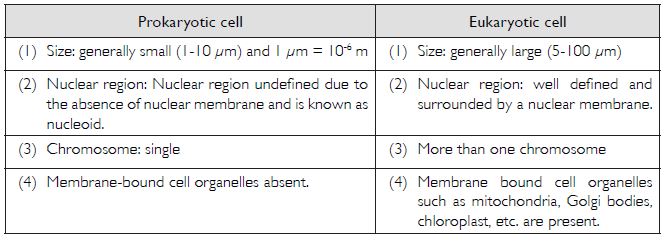
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
Question 6:
Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:
The two cell organelles that contain their own genetic material are mitochondria and plastids.
Question 7:
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed, it will stop performing basic functions and will ultimately die. lysosomes present inside the cell will burst to release enzyme which will digest the cell.
Question 8:
Why lysosomes are known as suicide bags?
Answer:
Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs filled with powerful digestive enzymes. If a cell gets damaged, lysosomes burst and the enzymes present in them digest the contents & their own cells. Hence, lysosomes are called the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell.
Question 9:
Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer:
Proteins are synthesised in the ribosomes that are attached to the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum or lie freely in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes are also called ‘protein factories’ of the cell.
Question 10:
Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:
Question 11:
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
Refer (In-Text-Question) Question 1 Page 63
Question 12:
What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or break down?
Answer:
Plasma membrane maintains the shape of a cell and protects the cell organelles. If it gets ruptured, the cell will die and its contents will get disintegrated.
Question 13:
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
The absence of Golgi apparatus will affect the life of a cell in the following ways:
(a) Golgi apparatus performs the functions of storage, modification and packaging of
materials synthesised in the cell. These materials will not be able to perform their
function in the absence of Golgi apparatus.
(b) The formation of lysosomes will be affected.
Question 14:
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:
Mitochondria are known as powerhouse of the cell. They are the sites for the synthesis, storage and transport of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), commonly called ‘energy currency’ of the cell.
Question 15:
Where do lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
(a) Proteins are synthesised by the ribosomes attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum.
(b) Lipids are synthesised by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
(c) These proteins and lipids are modified by the Golgi apparatus to form the plasma
membrane.
Question 16:
How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
Amoeba obtains its food by the process of endocytosis. In this process, food is ingested through the plasma membrane. This happens due to flexible nature of the plasma membrane, which enables Amoeba to engulf the food and other materials from its surroundings.
Question 17:
What is osmosis?
Answer:
Osmosis is a special case of diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. It is the movement of water from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
Question 18:
Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these
potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each
Answer:
(a) The water gathers in the hollowed portion of potato cups B and C due to osmosis.
(b) Cup A is necessary because it shows that if two solutions have the same concentration,
there is no net movement of water molecules.
(c) Water does not gather in the hollowed portion of A because there is no change in the
concentration of water. For osmosis to occur, one of the concentrations must be higher.
(d) Cup D was made of dead cells and their cell membranes were no more selectively permeable
membranes. Therefore no osmosis takes place and water does not get collected in cup D.
Question 19:
Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Answer:
Mitosis cell division is required for growth and repair of body and meiosis cell division is involved in gametes formation.