Question 1:
What do you understand by ‘people as a resource’?
Answer:
‘People as a resource’ is a way of referring to the working population of a country, in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities. A large population is considered as a liability, rather than an asset. However, a large population can be turned into a productive asset by investing in education, training and the medical care of the people. A productive population contributes considerably towards creation of Gross National Product. ‘People as a resource’ is the positive side of a large population that is often overlooked.
Question 2:
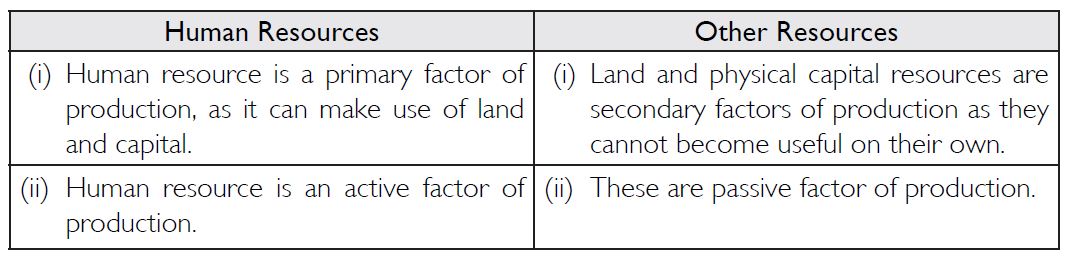
How is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Answer:
The following are the main differences between human resources and other resources such as land and physical capital:
Question 3:
What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Answer:
(i) An educated society facilitates better development than an illiterate one.
(ii) Education provides new aspirations and imparts a modern outlook to children.
(iii) Education makes people concerned for themselves and others, improves productivity and
prosperity, and enriches life experience.
(iv) It not only contributes towards the growth of an individual but also helps in the
development of
the society as a whole.
(v) Along with increasing the efficiency of the government, education also increases the
national
income along with our cultural richness.
Question 4:
What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Answer:
Health does not mean survival only. It involves not only the physical fitness of the
individual but also
his mental capabilities. Health contributes towards human capital formation in the following
ways:
(i) A healthy person provides uninterrupted labour supply for a longer period than an
unhealthy
person.
(ii) The health of a person helps him to realise his potential and ability to fight
illness.
(iii) Good health increases the efficiency of a worker.
(iv) Good health increases the learning capacity of a worker.
Question 5:
What part does health play in the individual’s working life?
Answer:
Health plays an important role in an individual’s working life. A healthy person provides uninterrupted labour supply for a longer period than an unhealthy person. Good health helps him to discover his true potential and his ability to fight illness along with increasing the efficiency of a worker.
Question 6:
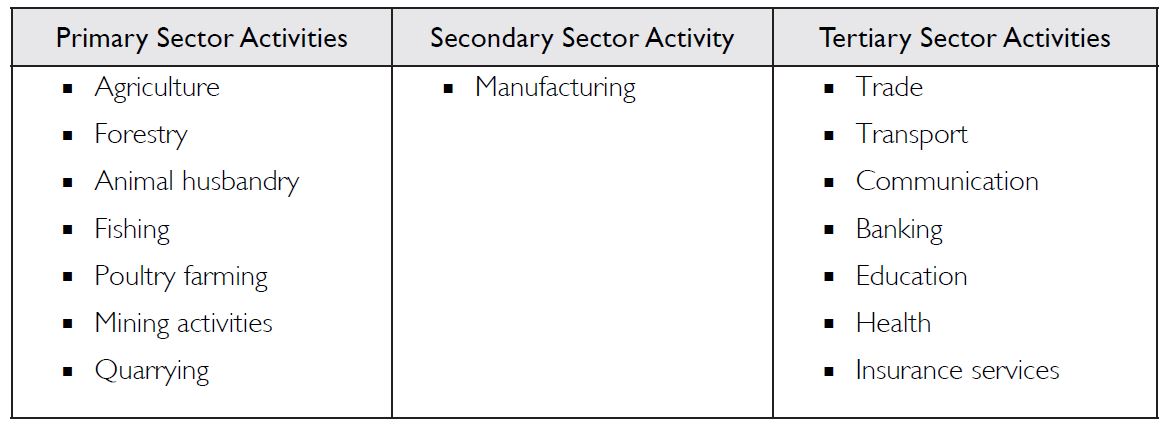
What are the various activities undertaken in the primary, secondary and the tertiary sectors?
Answer:
The various activities undertaken in the primary, secondary and the tertiary sectors are classified in the table below:
Question 7:
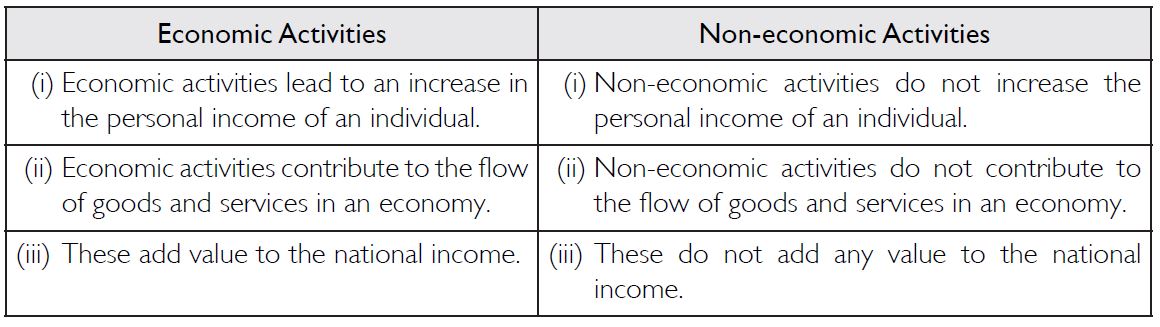
What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Answer:
Following are the main points of difference between economic activities and non-economic activities:
Question 8:
Why are women employed in low paid work?
Answer:
Women are employed in low paid work due to the following reasons:
- There is a division of labour between men and women due to the historical and cultural reasons.
- Among women, the literacy rate and skill formation are low.
- The legal protection of women employees is meager.
- Most women find jobs in fields, where there is no job security.
Question 9:
How will you explain the term unemployment?
Answer:
Unemployment is a situation when a person is not involved in any gainful occupation. It also exists when a person is able and willing to work, but cannot find jobs It creates a feeling of despair among the educated youth. It has a negative impact on the overall economic growth of a country.
Question 10:
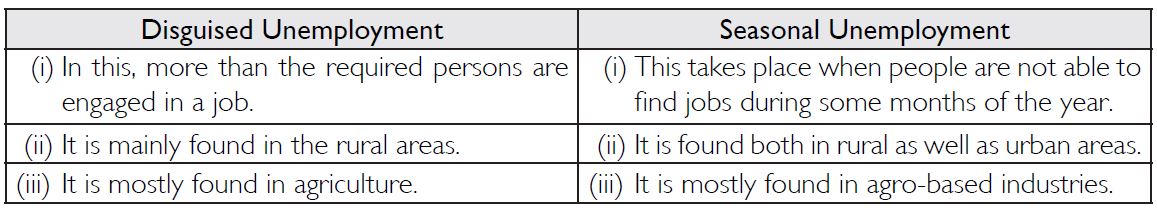
What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Answer:
Following are the main points of difference between disguised and seasonal unemployment:
Question 11:
Why is educated unemployment, a peculiar problem of India?
Answer:
Educated unemployment is a peculiar problem of India due to the following reasons:
- There is unemployment in the technically qualified population, while there is a scarcity of technical skills required for the economic growth of a country.
- According to a study, unemployment among graduates and post graduates has increased faster than the matriculates.
- In a paradoxical manpower situation, there is surplus manpower in certain categories while there is shortage of manpower in others.
- Not being able to find job for long periods creates a feeling of depression among the youth.
Question 12:
In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity?
Answer:
Most of the population is engaged in the agriculture sector. India can develop employment opportunities in the field of primary sector by introducing modern methods of cultivation and production. The government can also ensure employment in secondary and tertiary sectors by focusing on skill development and the training of individuals.
Question 13:
Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Answer:
Following are some of the measures that can be undertaken to mitigate the problem of educated unemployment:
- Educational institutions should focus on imparting job-oriented education.
- The structure of education should be such that it successfully caters to the employment market.
- Vocational and professional education should be promoted to introduce the future prospects of various career opportunities to the youth.
- The students should be provided educational counselling to help them identify their areas of interest and persuade them to pursue their career in the same.
Question 14:
Can you imagine some village which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
Answer:
There are a large number of villages in India which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many jobs. The generation of different types of employment opportunities takes place with the development of industry and infrastructure near a village. Gurgaon is one of the most appropriate examples. Prior to the setting up of the Maruti Udyog Limited in Gurgaon, it was a small village. However, with subsequent development of the industry, Gurgaon has now been converted into an international business hub.
Question 15:
Which capital would you consider the best—land, labour, physical capital and human capital? Why?
Answer:
Among land, labour, physical capital and human capital, human capital is the best because it can make use of land, labour and physical capital. Land and capital cannot become useful on their own.
Question 16:
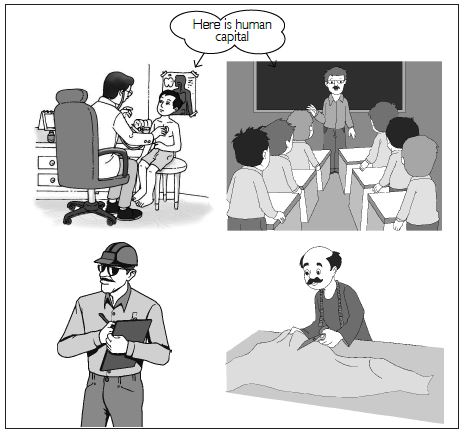
Looking at the photograph can you explain how a doctor, teacher, engineer and tailor are an asset to the economy?
Answer:
A doctor, teacher, engineer and tailor are assets to the economy as they all contribute
towards the
creation of a country’s Gross National Product.
(i) A doctor cures the patients and makes them able to do work.
(ii) A teacher enables the people to read, write and understand. This enables them to work
in
different fields.
(iii) An engineer formulates human capital by making roads, bridges and building.
(iv) A tailor converts raw material into finished products, which can be bought and used by
the
people.
Thus, all of them in their own way contribute towards the economic development of the
country.
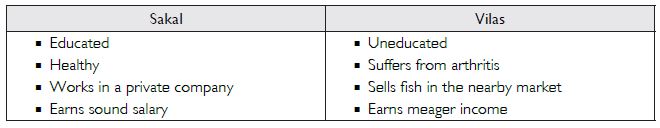
Question 17:
Do you notice any difference between the two friends (Sakal and Vilas)? What are those?
Answer:
The following differences have been noticed between the two friends Vilas and Sakal:
Question 18:
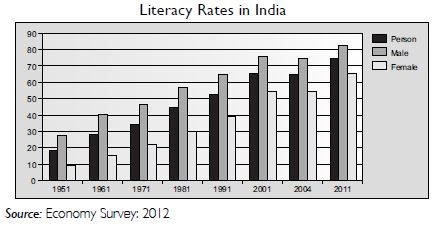
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951?
Answer:
Yes, the literacy rate of the population has increased from 28 per cent in 1951 to 74 per cent in 2010–11.
Question 19:
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
In which year India has the highest literacy rates?
Answer:
India has the highest literacy rate in the year 2011.
Question 20:
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
Answer:
The literacy rate is high among the males of India due to the gender inequalities which are present in the Indian society.
Question 21:
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
Why are women less educated than men?
Answer:
Our history and culture has always differentiated between man and woman. The man is considered to be the bread-earner of the family, whereas the woman is supposed to do house-hold chores and look after the family. Hence, female education was neglected. However, with changing times, this mindset has also changed now-a-days. The level of education among women is also rising.
Question 22:
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
How would you calculate literacy rate in India?
Answer:
Literacy rate in India is calculated by taking the ratio of educated population to the total population and multiplying it by 100.
Question 23:
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
What is your projection about India’s literacy rate in 2020?
Answer:
By 2020, at least 80 per cent of India’s population should be literate.
Question 24:
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions:
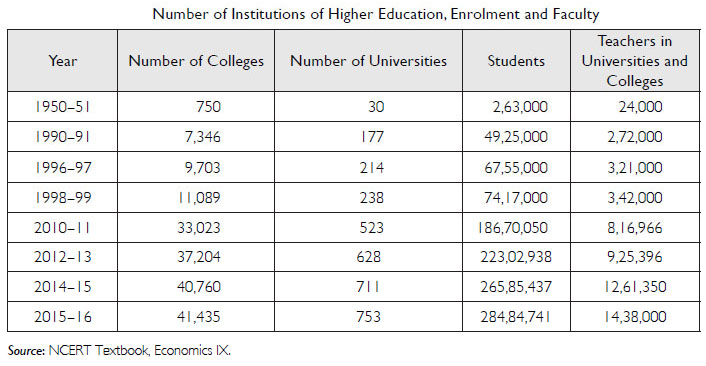
Is the increase in number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of students?
Answer:
No, from the data of 2015–16, it can be observed that the increase in the number of colleges is not adequate to admit the ever increasing number of students.
Question 25:
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions:

Do you think we should have more number of universities?
Answer:
Yes, we should have more universities. However, we have to keep in mind that the quality does not deteriorate as quantity increases.
Question 26:
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions:

What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99?
Answer:
The number of teachers increased from 3,21,000 in 1996–97 to 3,42,000 in 1998–99, that is, 6.54 per cent.
Question 27:
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions:

What is your idea about future colleges and universities?
Answer:
A large number of private colleges are being introduced. However, the quality of education does not meet the required standards. There is high absenteeism among the students. Teachers are not qualified enough. Steps must be taken to ensure the quality of colleges and universities as these institutions prepare the future of our country.
Question 28:
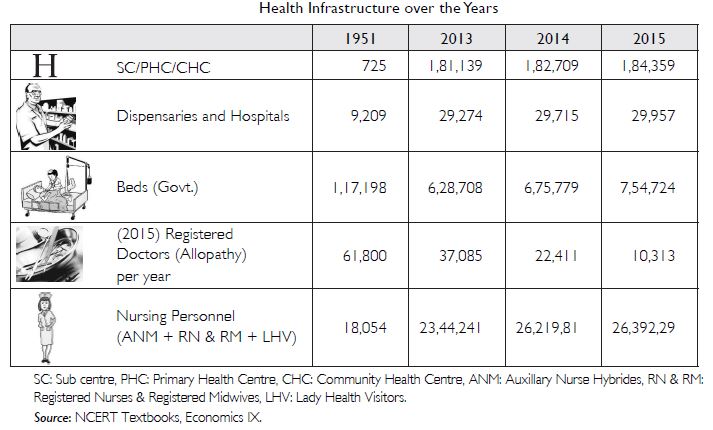
Study the Table and answer the following questions:
What is the percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2015?
Answer:
The percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2015 can be calculated as:
(29,957 – 9209) 9209 X 100
= 2074800/9209
= 225.3%
The dispensaries increased by 225.3 per cent from 1951 to 2015.
Question 29:
Study the Table and answer the following questions:
Do you think the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is adequate for India? If not, why?
Answer:
No, the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is not adequate with regards to India. The rate of increase in population is much higher than the rate of increase in the number of doctors and nurses.
Question 30:
Study the Table and answer the following questions:
What other facilities would you like to provide in a hospital?
Answer:
The following facilities should be available in all government hospitals:
(i) X-ray and ultrasound equipments
(ii) More doctors and nurses
(iii) Sufficient beds
(iv) House-keeping staff to maintain hygiene and cleanliness in the hospitals
(v) Efficient administrative staff