Question 1:
A landmass bounded by sea on three sides is referred to as:
- Coast
- Island
- Peninsula
- None of these
Answer:
(c) Peninsula
Question 2:
Mountain ranges in the eastern part of India forming its boundary with Myanmar are collectively called:
- Himachal
- Uttarakhand
- Purvanchal
- None of these
Answer:
(c) Purvanchal
Question 3:
The western coastal strip, south of Goa, is referred to as:
- Coromandel
- Konkan
- Kannad
- Northern circar
Answer:
(b) Konkan
Question 4:
The highest peak in the Eastern Ghats is:
- Anai Mudi
- Kanchenjunga
- Mahendragiri
- Khasi
Answer:
(c) Mahendragiri
Question 5:
What is the Bhabar?
Answer:
Bhabar is a long narrow plain along the foot hills. It is pebble studded zone (8–16 km
wide).
Rivers are lost in this region.
Question 6:
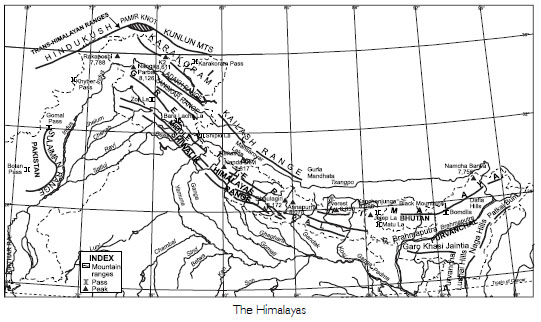
Name the three major divisions of the Himalayas from north to south.
Answer:
The Himalayas have been uplifted by different mountain building movements. There are many
parallel mountain ranges in the Himalayas. These ranges are separated from each other by
longitudinal
valleys called ‘Duns’. These ranges suggest different stages of folding. According to
height, the different
ranges are:
(a) The Great Himalayas or Inner Himalayas. (b) The Lesser Himalayas or Middle Himalayas.
(c) The Shiwaliks or Outer Himalayas.
Karakoram ranges and Ladakh ranges are Trans-Himalayan ranges running parallel to one
another.
Zanskar ranges form the Great Himalayas. The lesser Himalayas in the form of Pir Panjal
ranges
and Dhauladhar ranges belong to middle Himalayas. The southernmost ranges of the Himalayas
are
known as the Shiwalik ranges.
Question 7:
Which plateau lies between the Aravali and the Vindhyan ranges?
Answer:
Malwa Plateau
Question 8:
Name the island group of India having coral origin.
Answer:
Lakshadweep
Question 9:
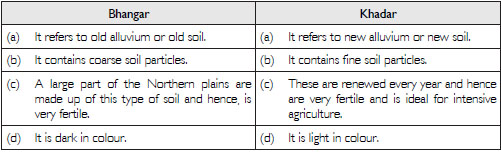
Distinguish between:
Bhangar and Khadar
Answer:
Question 10:
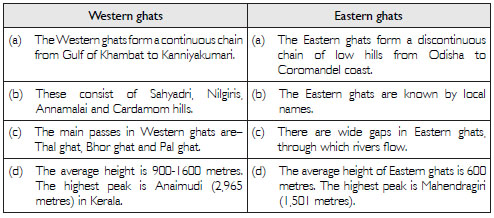
Distinguish between:
Western ghats and Eastern ghats.
Answer:
Question 11:
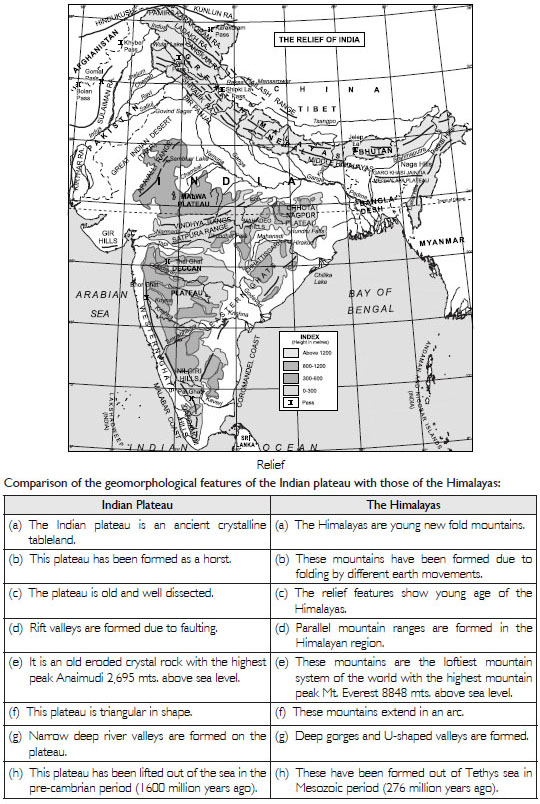
What are the major physiographic divisions of India? Contrast the relief of the Himalayan region with that of the Peninsular Plateau.
Answer:
India is a vast country where severe contrasts are found in relief. India is divided into 6
independent
physiographic divisions:
(i) The Great Mountain Wall of the North; (ii) The Northern Plains; (iii) The Great
Peninsular Plateau;
(iv) The Great Indian Desert; (v) The Coastal Region; (vi) Islands.
Question 12:
Give an account of the Northern Plains of India.
Answer:
Northern Plains of India
The Great Plain extends in between the Himalayas and the Peninsular Plateau extending from
Punjab
Plains to Assam Valley. It is 2,400 km long and 240 to 320 km wide. Its average height is
150 metres.
It covers an area of 7.5 lakh sq. km.
Division of Northern Plain
(i) Bhabar and Terrai: It is a long, narrow zone along the foothills. It is a pebble studded
zone.
Swampy areas occur in Terai.
(ii) Punjab Plain: This plain has a slope in the South-West direction. It has been formed by
the
deposition of sediments by Ravi, Beas and Sutlej rivers. Chos (Seasonal streams) cause soil
erosion in the foothills of Shiwaliks.
(iii) Ganga Plain: This plain has been formed by the deposition of sediments brought by the
Ganga
and its tributaries. It can be divided into three regions–upper Ganga plain, middle Ganga
plain and
the lower Ganga plain. It occupies an area of about 3.5 lakh sq. km. Sunderban Delta is
formed
in the lower Ganga plain. This fertile delta is the largest delta of the world.
(iv) Brahmaputra Plains: These plains are situated in the eastern part and are often known
as Assam
valley. The Brahmaputra river forms a large delta in Bangladesh. The river forms a narrow,
deep
gorge ‘Dihang gorge’ which is 12,000 metres deep.
Question 13:
Write short notes on the following:
(i) The Indian Desert
(ii) The Central Highlands
(iii) The Island Groups of India
Answer:
(i) The Indian Desert lies towards the western margin of the Aravallis. It is a sandy plain
with the
dunes. It has low rainfall of 150 mm. It has low vegetation cover and it has an arid
climate.
(ii) The central highlands form the oldest structure of India. It is an ancient, stable,
hard block formed
by igneous and metamorphic rocks. It was a part of Gondwana land. The mountain ranges
consist
mostly of residual mountains. The plateaus consist of long narrow ridges which are
storehouse
of minerals.
(iii) There are about 550 islands in the Indian Ocean. Most of these islands are too small
to be
inhabited. These islands are found in the following groups:
(a) Andaman and Nicobar islands: These islands form two major groups in the Bay of Bengal.
These are Andaman and Nicobar islands. These islands extend between 6 and 14 N
latitudes for a distance of 500 kms and are 214 in number. The Nicobar group consists of
15 islands extending between 6 N to 10 N latitudes. Ten degree channel separates the
Andaman group of islands from the Nicobar group. These islands form a Union Territory
of India with Port Blair as its capital. Indira Point in the Nicobar island in the
southernmost
point of the Indian Union. These islands form the summits of the submerged hills of the
ocean floor. Barren islands and Narcondam islands, situated in north of Port Blair are
volcanic
islands. Barren island is the only active volcano in India which erupted on 10th April
1991.
(b) Lakshadweep islands. These islands are situated in the Arabian Sea and lie 320 km off
the
coast of Kerala between 8 and 12 North latitudes. These are coral islands and some of these
are ring shaped and called atolls. These are 27 in number and 17 of these are uninhabited.
It
is a U.T. with Kavarti as its capital. Pamban and Rameshwaram islands lie between India and
Sri Lanka.
Question 14:
The names of the glaciers and passes that lie in Great Himalayas.
Answer:
Names of the glaciers
(a) Siachen Glacier–Ladakh
(b) Godwin Glacier–Ladakh
(c) Gangotri Glacier–Uttarakhand
(d) Yamunotri Glacier–Uttarakhand
Names of the passes
(a) Khyber Pass lies in the Safed Koh range of mountains connecting Peshawar in Pakistan
with Kabul
in Afghanistan.
(b) Shipkila Pass lies along Tibet border in Himachal Pradesh.
(c) Nathula Pass lies between Sikkim and China border.
(d) Zojila Pass connects Tibet to Srinagar.
(e) Bomdila Pass lies on Arunachal Pradesh-China border.
(f) Banihal Pass, south of Karakoram makes mountain journey possible.
(g) Lipu-Lekh Pass lies on U.P. -Tibet border.
Question 15:
The name of the states where highest peaks are located.
Answer:
Many high peaks include Kanchenjunga (8,598 metres) in Sikkim, the highest Himalayan peak in India.
