Question 1:
Migrations change the number, distribution and composition of the population in:
- the area of departure
- the area of arrival
- both the area of departure and arrival
- none of the above
Answer:
(c) both the area of departure and arrival
Question 2:
A large proportion of children in a population is a result of:
- high birth rates
- high life expectancies
- high death rates
- more married couples
Answer:
(a) high birth rates
Question 3:
The magnitude of population growth refers to:
iii) The magnitude of population growth refers to:
- the total population of an area
- the number of persons added each year
- the rate at which the population increases
- the number of females per thousand males.
Answer:
(b) the number of persons added each year
Question 4:
According to the census, a ‘literate’ person is one who:
- can read and write his/her name
- can read and write any language
- is 7 years old and can read and write any language with understanding
- knows the 3 R’s (reading, writing, arithmetic)
Answer:
(c) is 7 years old and can read and write any language with understanding
Question 5:
Why is the rate of population growth in India declining since 1981?
Answer:
The rate of population growth in India is declining since 1981, on account of the following
reasons:
(a) Better healthcare facilities provided by the government.
(b) A sharp decline in birth as well as in death rates.
Question 6:
Discuss the major components of population growth.
Answer:
Population growth depends upon the following components:
(a) Birth rate (b) Death rate (c) Migration.
(a) Birth rate is the number of live births in a year per 1000 of the population of an area.
At present,
the birth rate in India is 21.8.
(b) Death rate is the number of deaths in a year per 1000 of the population of an area. At
present,
the death rate of India is 7.1.
(c) Migration refers to the process of moving from one place to another, permanently or for
a
longer period of time. It affects the change in number of distribution and composition of
the
population both in the area of departure and arrival.
Question 7:
Define age structure, death rate and birth rate.
Answer:
Age Structure: It refers to the division of population into three categories of age groups.
These
categories are:
(a) Change in the age-group of below 15 years.
(b) Adults or working population in 15–65 years of age group.
(c) Old group in the age group 65 year and above.
Birth rate: It refers to the number of live births in a year per 1000 of the population of
an area.
At present, the birth rate in India is 21.8.
Death rate: It refers to the number of deaths in a year per 1000 of the population of an
area.
At present the death rate of India is 7.1.
Question 8:
How is migration a determinant factor of population change?
Answer:
Migration means the movement of people across areas. It can be internal as well as external.
Migration
from rural areas takes place due to rising population and the lack of demand for
agricultural labour.
Moreover, cities offer better amenities, infrastructure, better standard of living and
better economic
opportunities.
Question 9:
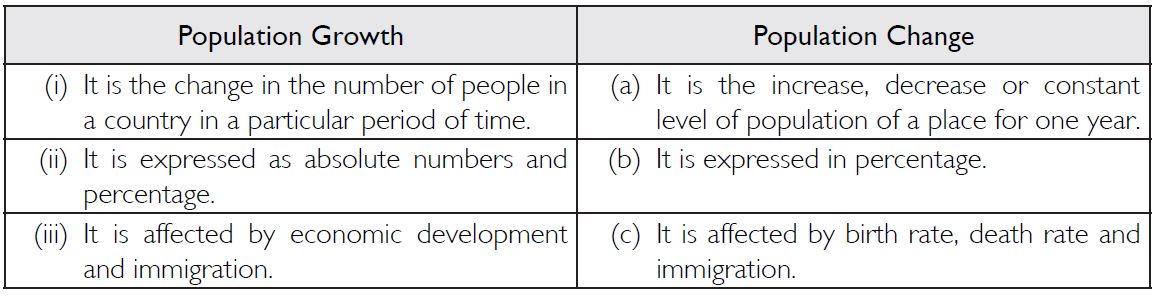
Distinguish between population growth and population change.
Answer:
Question 10:
What is the relation between occupational structure and development?
Answer:
Occupational structure refers to the distribution of its people according to different
occupations.
Primary occupations include agriculture, animal husbandry, forestry and fishery.
Manufacturing is a
secondary occupation. Tertiary occupations include transport, communication, banking,
service, etc.
Question 11:
What are the advantages of having a healthy population?
Answer:
Manpower is a vital resource of a country. The human resources or number of people constitute
its
manpower. Manpower exploits the natural resources of a country. Sparse population is a
hindrance
in the development of some countries. But manpower is not assessed in human number
alone.
Manpower is assessed by the quality of the people.
An interaction between man and his environment results in the utilisation of resources.
Thus, the
economic standard of a country is raised. Manpower must be educated, efficient, skilled and
gifted with
scientific knowledge. Healthy, hardworking, capable and energetic people make the real
manpower.
Such manpower produces more and increases the gross national production of a country. Hence,
manpower is assessed in terms of quality and not in quantity.
Question 12:
What are the significant features of the National Population Policy 2000?
Answer:
National population policy was implemented in year 1952. Its main objectives are to:
(i) Promote the economic and social development of the country and improve the quality of
life of
people.
(ii) To enhance their well-being and to provide them with opportunity and choices to become
productive assets in society.
(iii) Death rate is to be reduced. Family planning and birth control measures are to be
used.
The National Population Policy (NPP) aims at stabilising population by 2045. It lays
emphasis on
economic growth, social development, and environmental protection. Certain measures which
are to
be adopted for it are:
(i) Raising the age of marriage.
(ii) Making school education up to age of 14 years free and compulsory.
(iii) Reducing dropouts at primary and secondary levels.
Question 13:
What could be the reason of uneven distribution of population in India?
Answer:
Rugged terrain, water supply, employment opportunities, climatic conditions, means of communication and transportation, etc. could be the possible reason for the uneven distribution of population in India.
Question 14:
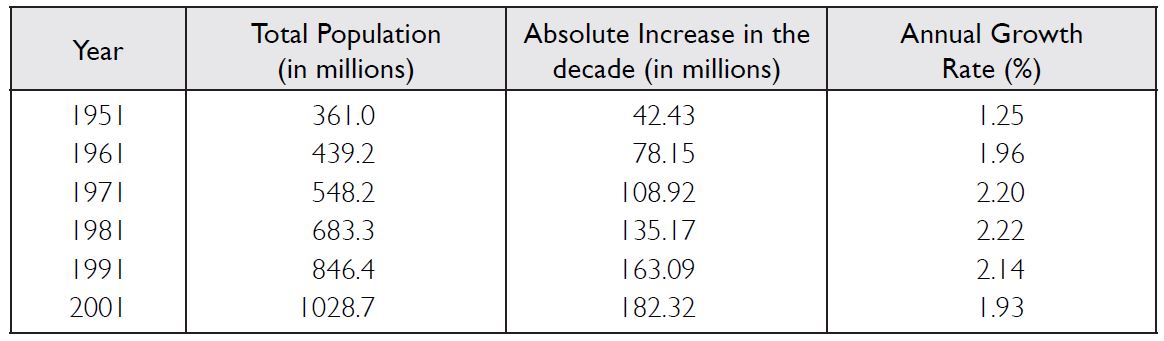
The table given below reveals that despite the decline in growth rates, the number of people being added every decade is steadily increasing. Why?
Answer:
The table reveals that from 1951 to 1981, the annual rate of population growth was steadily
increasing.
After 1981, the trend of annual growth rate of population began to decrease. The annual
rate, when
implied to a huge population results in the rapid increase in population.
The Magnitude and Rate of India’s Population Growth
Question 15:
What could be the reasons for such variations (in sex ratio)?
Answer:
Literacy plays a major role in the sex ratio of a country. India, being a male dominated society, prefers males over females; hence the female population is neglected. People also practice female infanticide and female foeticide, which leads to the declining sex ratio in India.