Question 1:
What is the common name of the compound
Answer:
Bleaching powder
Question 2:
Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer:
Dry slaked lime
Question 3:
Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer:
Washing soda
Question 4:
What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer:
It decomposes to give sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide gas (which is colourless, odourless and turns lime water milky).
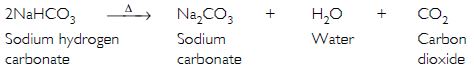
Question 5:
Write an equation to show the reaction between Plaster of Paris and water.
Answer:
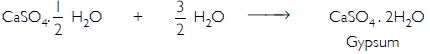
Question 6:
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be:
- 4 mL
- 8 mL
- 12 mL
- 16 mL
Answer:
16 mL
Question 7:
Why does not distilled water conduct electricity, whereas rainwater does?
Answer:
Distilled water does not conduct electricity because it does not contain any ions. Rainwater contains ions due to dissolved salts, hence it conducts electricity.
Question 8:
Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer:
Plaster of Paris gains moisture and sets into a hard mass known as gypsum. Therefore it must be stored in a moisture-proof container.
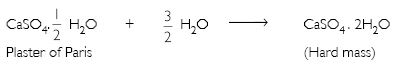
Question 9:
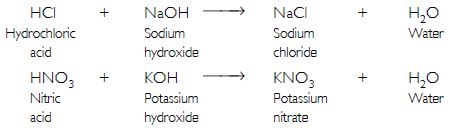
What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
Answer:
It is a reaction of an acid with a base to form a salt and water.
Question 10:
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer:
- Uses of washing soda:
- It is used in the manufacture of glass and soap.
- It is used in the manufacture of borax.
- Uses of baking soda:
- It is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher.
- It is used for making baking powder.
Question 11:
Match the important chemicals given in Column (A) with the chemical formulae given in Column (B).
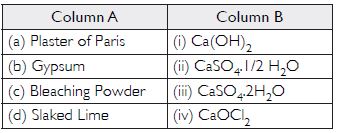
Answer:
- (ii)
- (iii)
- (iv)
- (i)
Question 12:
How would you distinguish between baking powder and washing soda by heating?
Answer:
Baking powder contains sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO3) and washing soda is sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H 2 O). Sodium hydrogencarbonate on heating gives CO2 gas which will turn lime water milky whereas no such gas is obtained from sodium carbonate decahydrate
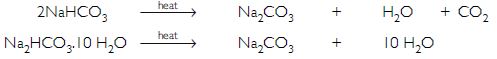
Question 13:
Salt ‘A’ commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt ‘B’ which itself is used for removal of hardness of water and a gas ‘C’ is evolved. The gas ‘C’ when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’.
Answer:
Salt ‘A’ is commonly used in bakery products hence it must be sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda). On heating it forms salt ‘B’ i.e. sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) which is used for the removal of hardness of water and the gas evolved is CO2 i.e. ‘C’. When CO2 gas is passed through lime water it forms calcium carbonate (CaCO3) thereby turning the lime water milky.
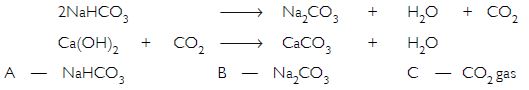
Question 14:
In one of the industrial processes used for manufacturing sodium hydroxide, a gas ‘X’ is formed as a by-product. The gas ‘X’ reacts with lime water to give a compound ‘Y’ which is used as a bleaching agent in chemical industry. Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’ giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is manufactured by the electrolysis of concentrated solution of sodium chloride called brine. The by-product is chlorine gas. Hence, gas X is chlorine. Chlorine reacts with lime water to give bleaching powder, which is used as a bleaching agent. Hence, Y is bleaching powder.
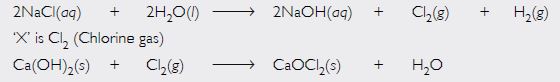
Question 15:
Fill in the missing data in the following table
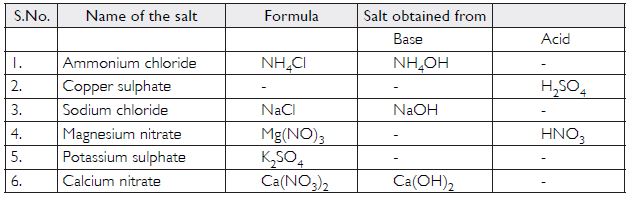
Answer:
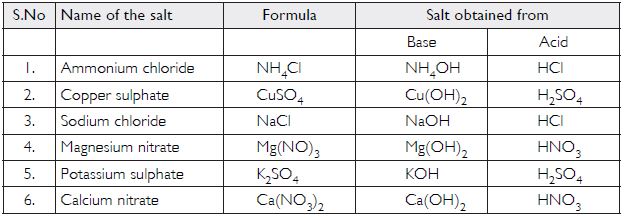
Question 16:
For making cake, baking powder is taken. If at home your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake,
- How will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
- How can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
- What is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
Answer:
- Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate. On heating, it is converted into sodium carbonate which is bitter to taste.
- Baking soda can be converted into baking powder by adding the appropriate amount of tartaric acid to it.
- The role of tartaric acid is to neutralise sodium carbonate and the cake will not taste bitter.
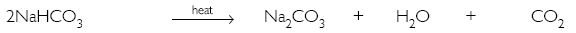
Question 17:
A metal carbonate ‘X’ on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution ‘Y’ gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas ‘G’ that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry ‘Y’. It gives a compound ‘Z’, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity ‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘G’ and ‘Z’.
Answer:
The gas evolved at anode during electrolysis of brine is chlorine (G). When chlorine gas is passed through dry Ca(OH)2 (Y) produces bleaching powder (Z) used for disinfecting drinking water.
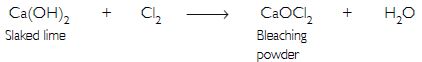
Since ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ are calcium salts, therefore ‘X’ is also a calcium salt and is calcium carbonate.
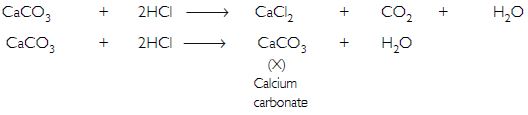
Question 18:
A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be moulded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in the open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for moulding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt and why does it show such a behaviour? Give the reaction involved.
Answer:
The substance which can be moulded into different shapes is plaster of Paris, CaSO4. When it is left open for some time, it absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and forms gypsum, which is a hard solid mass.
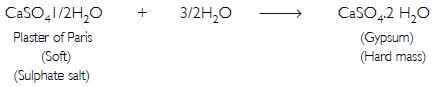
Question 19:
Zinc liberates hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, whereas copper does not. Explain why?
Answer:
Zinc lies above hydrogen whereas copper lies below hydrogen in the activity series of metals. Therefore, zinc displaces hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid, while copper does not.
Question 20:
You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and the pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer:
As the given pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Therefore, A has more hydrogen ion concentration. Solution A with pH less than 7 is acidic and solution B with pH more than 7 is basic.
Question 21:
What effect does the concentration of 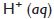
Answer:
Acidic nature of the solution increases on increasing the concentration of 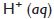
Question 22:
Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer:
If the pH of the soil is less than 7, i.e. it is acidic; the farmer will treat the soil with alkaline substances like quick lime, slaked lime, and chalk. For healthy growth of plants, the soil should neither be highly alkaline nor acidic.
Question 23:
A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be:
- 1
- 4
- 5
- 10
Answer:
10
Question 24:
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed the pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is
- neutral?
- strongly alkaline?
- strongly acidic?
- weakly acidic?
- weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
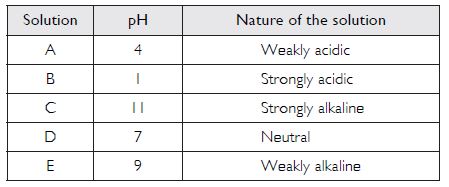
Answer:
The increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration is:
11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1 (pH values).
Question 25:
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer:
As the milk turns into curd its pH will decrease due to the production of lactic acid which is acidic in nature.
Question 26:
A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
- Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
- Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
Answer:
- Fresh milk is acidic in nature. On addition of very small amount of baking soda, milk becomes alkaline and does not turn sour easily.
- This milk takes a long time to set as curd because the presence of alkali does not allow it to become more acidic.
Question 27:
A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgot to label the solutions and litmus paper was not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
Answer:
Phenolphthalein can be used in place of litmus paper. Take small quantity of both solutions in two different test tubes. Add a few drops of phenolphthalein in each of them. The acid solution will remain colourless while the solution of base will become pink.
