Students can grab NCERT Solutions for free on the Aasoka platform. During exam time, students are often confused about which material to study. Therefore, our team of experts has designed NCERT Solutions for Class 10th as per students’ requirements and by following the latest syllabus and exam pattern. Access the NCERT Solutions on Aasoka and get started with board exam preparation.
Through the “Agriculture” chapter, students of Class 10th will get to know about the various types of farming systems that are practiced in India, major crops produced in India, and their cropping patterns. India is known as an agricultural country and in this country, farming is practiced for ages.
Question 1:
Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
- Shifting agriculture
- Plantation agriculture
- Horticulture
- Intensive agriculture
Answer:
(b) Plantation agriculture
Question 2:
Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
- Rice
- Gram
- Millets
- Cotton
Answer:
(b) Gram
Question 3:
Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
- Pulses
- Jowar
- Millets
- Sesamum
Answer:
(a) Pulses
Question 4:
Answer following questions in 30 words.
Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Answer:
Tea is a beverage crop.
Geographical conditions for growth:
- It grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climatic conditions.
- It needs 20º–30ºC temperature throughout the year
- It requires an annual rainfall of 150 cm to 300 cm.
- It needs a frost free climate.
- It needs deep, fertile well drained soils rich in humus and organic matter.
- Tea is a labour-intensive crop and requires cheap and abundant skilled labour.
Question 5:
Answer following question in 30 words.
Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Answer:
Rice is the staple crop for people of India. It is grown in the following areas:
- Plains of Ganga and Brahmaputra.
- Coastal plains.
- Tarai region.
- Deltaic regions.
Question 6:
Answer following question in 30 words.
Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Answer:
- Collectivisation
- Abolition of Zamindari and Jagirdari
- Land ceiling
- Consolidation of land holdings
- Credit reforms
- Farmers rights
Question 7:
Answer following question in 30 words.
‘The land under cultivation has reduced day-by-day.’ Can you imagine its consequences?
Answer:
There has been a gradual shift from cultivation of food crops to cultivation of fruits, vegetables and oilseeds. This has resulted in the reduction of net sown area for food crops. The competition for land between non-agricultural uses, such as housing, etc., and agriculture has resulted in the reduction in the net sown area.
Question 8:
Answer the following question in 120 words.
Suggest the initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Answer:
The government has taken the following steps to increase agricultural production:
- HYV seeds have been introduced.
- Organic fertilisers and manures are being used on a large-scale.
- Intensive agriculture in irrigated areas has been encouraged.
- Green Revolution techniques have been introduced.
- Primitive methods have been replaced by modern techniques.
- Agricultural reforms like crop insurance, co-operatives, Kisan credit card and the announcement of minimum support prices.
Question 10:
Answer the following question in 120 words.
Describe the impact of globalisation on Indian agriculture.
Answer:
Indian Agriculture underwent many changes under globalisation. Indian farmers faced new challenges. Despite being leading producers of major crops, India could not compete with the international markets. After globalisation, Indian farmers started to practice organic farming and the cropping pattern changed from cereals to high-value crops.
Question 11:
Answer the following question in 120 words.
Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer:
Rice is a tropical crop.
- It grows well in hot and humid climate.
- It is essentially a Kharif crop in India.
- It requires high temperature, about 25°C and annual rainfall above 100 cm.
- In areas of low rainfall, it is grown with the help of irrigation.
- It is grown in alluvial soils of north and north-eastern plains coastal areas, southern plains and deltas.
- It requires cheap and abundant labour.
Question 12:
Can you name some industries based on agricultural raw material.
Answer:
Industries based on agricultural raw materials are cotton textile industry, woollen and textile industries, jute industries, paper industry, oil seed industries, etc.
Question 13:
‘Rinjha lived with her family in a small village at the outskirts of Diphu in Assam. She enjoys watching her family members clearing, slashing and burning a patch of land for cultivation. She often helps them in irrigating the fields with water running through a bamboo canal from the nearby spring. She loves the surroundings and wants to stay here as long as she can, but this little girl has no idea about the declining fertility of the soil and her family’s search for fresh patch of land in the next season.’
Can you name the type of farming Rinjha’s family is engaged in? Can you enlist some crops which are grown in such farming?
Answer:
Rinjha’s family is engaged in Jhumming farming. Crops such as Jowar, millets, beans, cassava, etc., are grown in such farming.
Question 14:
Can you name some of the states of India where intensive subsistence farming is practised?
Answer:
Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal and Gujarat are some states where this type of farming is practised.
Question 15:
Can you give some more examples of crops which may be commercial in one region and may provide subsistence in another region?
Answer:
Crops—Wheat and maize
- Commercial Crop: Wheat in Haryana, Punjab and Madhya Pradesh.
- Subsistence Crop: Maize in Haryana, Punjab and Madhya Pradesh.
Question 16:
Can you distinguish which of these pulses: tur, urad, moong, masur, peas and gram, are grown in Kharif and which are grown in the Rabi seasons.
Answer:
- Pulses grown in Rabi season are: Tur, Masur, Peas and Gram
- Pulses grown in Kharif seasons are: Urad and Moong
Question 17:
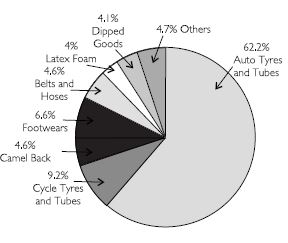
List the items which are made of rubber and used by us.
Answer:
Some of these items are foot wears, belt and hoses, dipped goods, cycle and auto tyres, along with tube.
Question 18:
Why are farmers committing suicides in several states of the country?
Answer:
- Due to heavy indebtedness
- Crop failure due to flood or adverse climatic conditions.
Question 19:
Can you name any gene modified seed used vastly in India?
Answer:
The gene modified seed used vastly in India is cotton.