Students of Class 10th can start preparing for their exams with the help of top NCERT Solutions at Aasoka. We offer questions and their solutions which are curated by a team of experts keeping the latest NCERT syllabus in mind. Students will get a clear understanding of all the topics which are related to the chapter. Get started with exam preparation with the best NCERT Solutions for Class 10th.
The chapter “Resources and Development” explains the classification of resources based on ownership, origin, the potential for development, and exhaustibility. From this chapter, students will get to know about the development of resources and resource planning. Also, there is a discussion about land resources with an in-depth description of land degradation and conservation measures, land utilization, soil as a resource, land use pattern in India, and classification of soil.
Question 1:
Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore?
- Renewable
- Biotic
- Flow
- Non-renewable
Answer:
(d) Non-renewable
Question 2:
Under which of the following type of resources can tidal energy be put?
- Replenishable
- Human-made
- Abiotic
- Non-recyclable
Answer:
(a) Replenishable
Question 3:
Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
- Intensive cultivation
- Deforestation
- Over irrigation
- Over grazing.
Answer:
(c) Over irrigation
Question 4:
In which of the following states is terrace cultivation practised?
- Punjab
- Plains of Uttar Pradesh
- Haryana
- Uttarakhand
Answer:
(d) Uttarakhand
Question 5:
In which of the following states predominantly black soil is found?
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Rajasthan
- Maharashtra
- Jharkhand
Answer:
(c) Maharashtra
Question 6:
Answer the following question in about 30 words.
Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Answer:
States with black soil:
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Madhya Pradesh.
Crop grown: Cotton.
Question 7:
Answer the following question in about 30 words.
What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main
features of this type of soil.
Answer:
Soil found in the Eastern Coastal Deltas: Alluvial Soil.
Main features of Alluvial Soil:
- Alluvial soils are very fertile.
- Due to its high fertility, these soils are intensively cultivated.
- These soils are rich in potash, phosphoric acid and lime.
Question 8:
What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Answer:
- Contour ploughing on slopes.
- Terraced cultivation restricts erosion.
- Strip cropping checks soil erosion.
- Planting of trees to form shelter belts.
Question 9:
What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Answer:
Biotic Resources: The living resources which sustain life are called biotic resources. Such as flora and fauna. Abiotic Resources: Resources which have no life but are essential for sustaining life are called abiotic resources. For example rocks and metals.
Question 10:
Answer the following question in about 120 words.
Explain land use pattern in India. Why has the land under forest not increased much from 1960–61?
Answer:
Land use in India (2008–09):
- Net sown area: India has a very high percentage (46.24%) of total area under cultivation.
- Fallow land: Only 3.37% of land is fallow land.
- Pastures: The area under pastures is small (3.38%).
- Cultivable waste: The area under cultivable waste is 4.17%
- Forests: The area under forests (22.78%) is not sufficient to maintain the ecological balance.
- Wasteland: The area under wasteland (8.16%) is increasing due to deforestation and over grazing.
- Forest area: The land under forests has not increased much from 1960-61.
Reasons:
- This is due to reckless deforestation.
- Due to increase in population, the forests have been cleared for cultivation and urbanisation.
Question 11:
Answer the following question in about 120 words.
How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer:
Resources have to be available for development. Due to absence of technology, many resource rich regions remain backward.
Reasons:
- Technology is used to exploit resources in India. The consumption of resources is increasing due to the use of technology and the quality of human resources in agriculture, mining and industries.
- With the use of technology, humans interact and modify nature and create institutions to increase the consumption of resources for economic development.
- Human made resources, like houses, buildings, roads, industries, etc. require more resources for consumption.
Question 12:
Have a discussion in the class–how to conserve various resources used in your school.
Answer:
Guidelines: Divide the class in groups. One group will discuss how to conserve water sources available in the school. The second group will discuss about the measures to conserve electricity in the school campus. The third group will discuss how to keep our surrounding environment neat and clean. The fourth group will put forward its view on conservation of other resources available in the school campus.
Question 13:
Imagine if oil supplies get exhausted, how will this affect our life style?
Answer:
If the oil supplies get exhausted, it will adversely affect our life style in the following ways:
- Without oil, it would be difficult to run industries.
- Transportation facilities would get effected. There will be no vehicles on the road.
- Agricultural production will suffer and come to a standstill.
Question 14:
Identify at least two resources from each category:
- Type of resources on the basis of origin:
- Type of resources on the basis of exhaustibility:
- Type of resources on the basis of ownership:
Answer:
(i) Type of resources on the basis of origin:
- Biotic resources: Human being and livestock
- Abiotic resources: Rocks and metal.
(ii) Type of resources on the basis of exhaustibility:
- Renewable resources: Solar and wind energy
- Non-renewable resources: Mineral and fossil fuels.
(iii) Type of resources on the basis of ownership:
- Individual resources: House and plots
- Community owned resources: Public parks and playing grounds.
- National resources: Forests and wildlife.
- International resources: All ocean resources beyond 200 nautical miles of the exclusive economic
zone belong to open ocean and no individual country can utilise these without the prior permission of international institution.
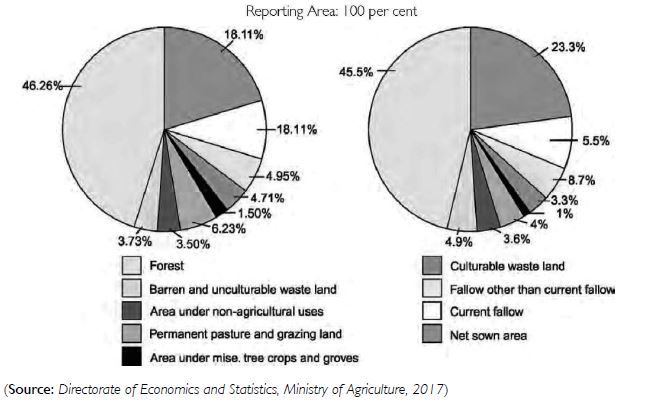
Question 15:
Try to do a comparison between the two pie charts given for the land use and find out why the net sown area and the land under forests have changed from 1960–61 to 2014–15 very marginally.
Answer:
(i) Change in net sown area
In 2014-15, net sown area was = 45.5%
In 1966-61, net sown area was = 46.26%
Changed in this year = 45.5 – 46.26
= –0.76%
(ii) Change in land under forest = 23.3 – 18.11%
= 5.19%
(Students to give explanation with the help of their teacher)